参考博客
开始之前,理解递归

手写 浅拷贝
function shallow(target){
if(target instanceof Array){
return [...resObj]
}else{
return Object.assign({},target);
}
}
手写深拷贝
const _sampleDeepClone = target => {
// 补全代码
return JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(target))
}
无法处理处理循环引用的问题
完整写法
function DeepCopy(target, map = new Map()) {
//对于普通类型 直接返回即可
if(typeof target!=='object' || target===null){return target}
//主要处理的是引用类型
let result = Array.isArray(target)?[]:{};
if (map.has(target)) {
result = map.get(target);
} else {
map.set(target, result);
for (let key in target) {
if (target.hasOwnProperty(key)) {
if (typeof target[key] === "object") {
result[key] = DeepCopy(target[key], map);
} else {
result[key] = target[key];
}
}
}
}
return result;
}
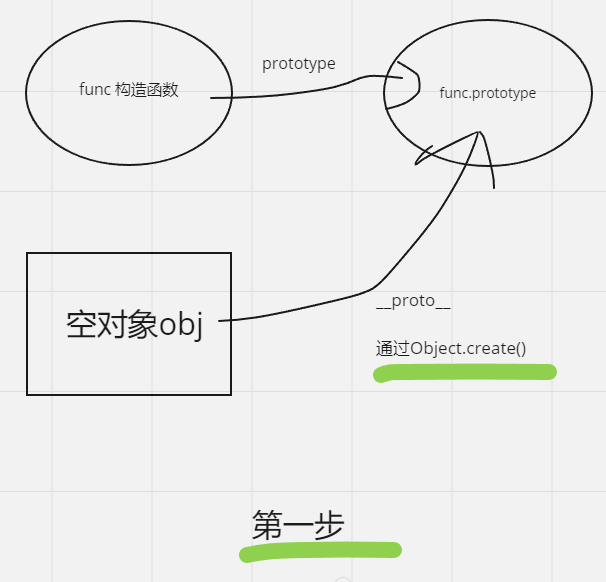
手写new
当你使用 new Person() 来调用构造函数 Person 时,它会创建一个新的对象,并将该对象的原型设置为 Person.prototype。这个新对象可以通过 this 关键字在构造函数内部访问和设置属性。
function Person(name, age){
this.name=name;
this.age=age;
return{
abc:'abc'
}
//mynew中最后的判断就是为了防止这种情况:构造函数会返回值,而不会创建新的实例
}
function myNew(func, ...args) {
//接受不确定长度的参数放到args数组中
if (typeof func !== "function") {
return new TypeError("fn must be a function");
}
//把新对象的__proto__指向func.prototype
let obj = Object.create(func.prototype);
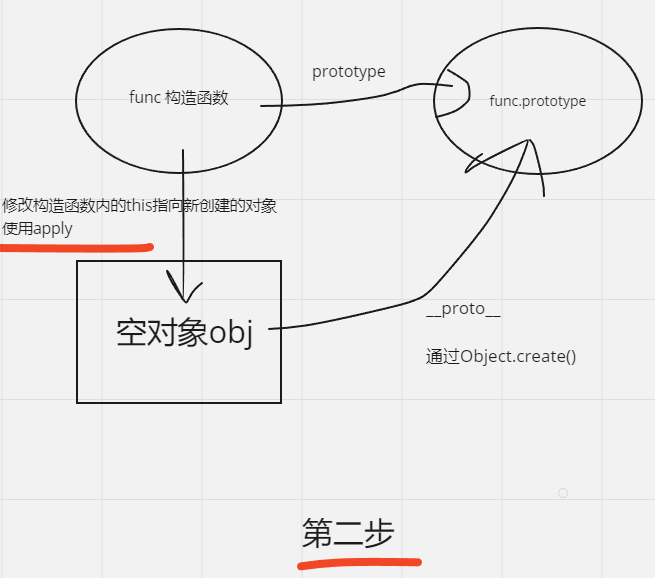
//构造函数内部的 this 值指向新创建的对象,从而在构造函数中正确地初始化新对象的属性和方法。
//apply会立即执行
//result接受执行结果
let result = func.apply(obj, args);
//如果构造函数有返回值,则返回这个返回值,没有的话返回新创建的对象
if (result && (typeof result === "object" || typeof result === "function")) {
return result;
} else {
return obj;
}
}
// const f1=new Person("xiaoming",22)
const f2= myNew(Person,"xiaoming",22)
console.log(f2);
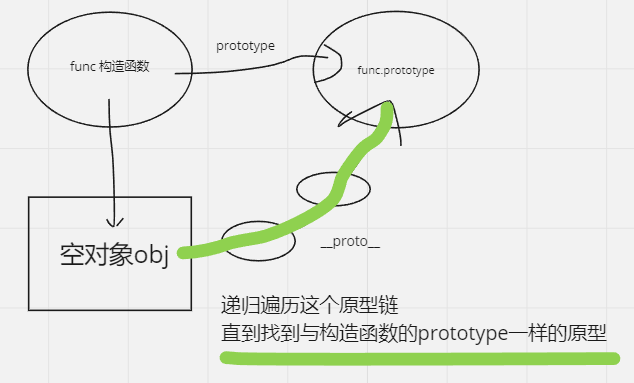
手写instanceof
function myInstanceof(obj,target){
//obj是被判断的对象
//target是一个构造函数
if(typeof obj!=='object'|| typeof target !== 'function'){
return new TypeError("inputs must be object type!")
}
let objProto = obj.__proto__
while(objProto!==null){
//注意这里用的是 构造函数.prototype
if(objProto===target.prototype) return true
objProto = obj.__proto__
}
return false
}
console.log(myInstanceof([1,2],Array));
Object.create
Object.create(proto)返回一个新对象,新对象的原型是proto
【可以不看】proto应该填入一个对象,而不是一个构造函数。
如果你使用 Object.create(Person),而不是 Object.create(Person.prototype)
person 对象的原型将直接设置为 Person 构造函数本身,而不是 Person 构造函数的原型。这意味着 person 对象将无法继承 Person.prototype 上的属性和方法。
这意味着 person 对象将继承 Function.prototype 上的属性和方法,而不是 Person.prototype 上的属性和方法。
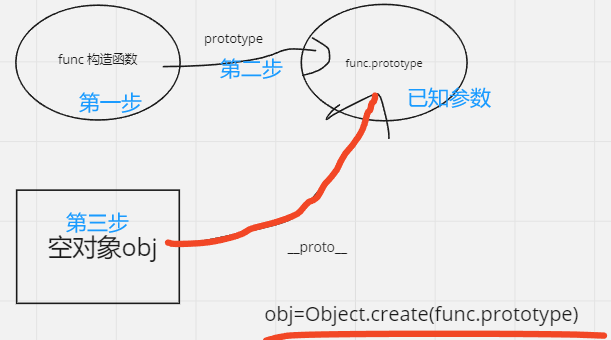
function myOBJcreate(proto){
function f(){}
f.prototype = proto
return new f()
}
const obj1={
name:'alice',
age:11
}
const f1 = Object.create(obj1)
const f2 = myOBJcreate(obj1)
//不需要比较,因为f1 f2是两个不同的对象
手写 防抖
主要思路:定时器控制1s后触发,并且保证只有一个定时器会被触发(timer的作用)
其实就是用定时器,来控制,这个函数只能1s后触发。
let Inp = document.querySelector("input");
function getValue() {
console.log(`获取${Inp.value}`);
}
Inp.addEventListener("keyup", debounce(getValue, 1000));
//业务代码
function debounce(func, time) {
let timer = null;
return function () {
if (!timer) {
timer = setTimeout(() => {
func.apply(this, arguments);
timer = null;
}, time);
}
};
}
如果你想传参:
let Inp = document.querySelector("input");
function getValue(name) {
console.log(`${name}获取${Inp.value}`);
}
newfunc = debounce(getValue, 1000);
Inp.addEventListener("keyup", ()=>{
newfunc("xiaoming")
});
function debounce(func, time) {
let timer = null;
return function () {
if (!timer) {
timer = setTimeout(() => {
func.apply(this, arguments);
timer = null;
}, time);
}
};
}
节流防抖巧记!
下面是业务代码,只有一行不同。
可以先把防抖的写出来(防抖的更容易理解),然后吧func.apply移出timer即可。
即节流第一次触发就要执行。
function debounce(func, delay) {
let timer = null;
return function () {
if (!timer) {
timer = setTimeout(() => {
func.apply(this, arguments);
timer = null;
}, delay);
}
};
}
const throttle = (func, delay) => {
let timer;
return function () {
if (!timer) {
func.apply(this, arguments);
timer = setTimeout(() => {
timer = null;
}, delay);
}
};
};
手写 节流(另一种方式,了解)
主要思路:判断上次触发的时间和这次的时间
使用方法是这样的:
const throttledFunction = throttle(myFunction, 1000); // 设置节流时间为1秒
throttledFunction就是一个具有节流功能的函数。你可以调用它来代替原始的myFunction函数。
const throttle = (func, delay) => {
let timer;
return function () {
if (!timer) {
func.apply(this, arguments);
timer = setTimeout(() => {
timer = null;
}, delay);
}
};
};
function test(name){
this.name = name;
console.log(`name is ${name}`);
}
let newfunc = throttle(test,5000)
newfunc('xiaoming') //只会运行1个
newfunc('xiaoming')
手写call
函数科里化的实现
前置:reduce方法:arr.reduce((accumulator, currentValue, currentIndex, array)=>{},初始值)
实现add函数:
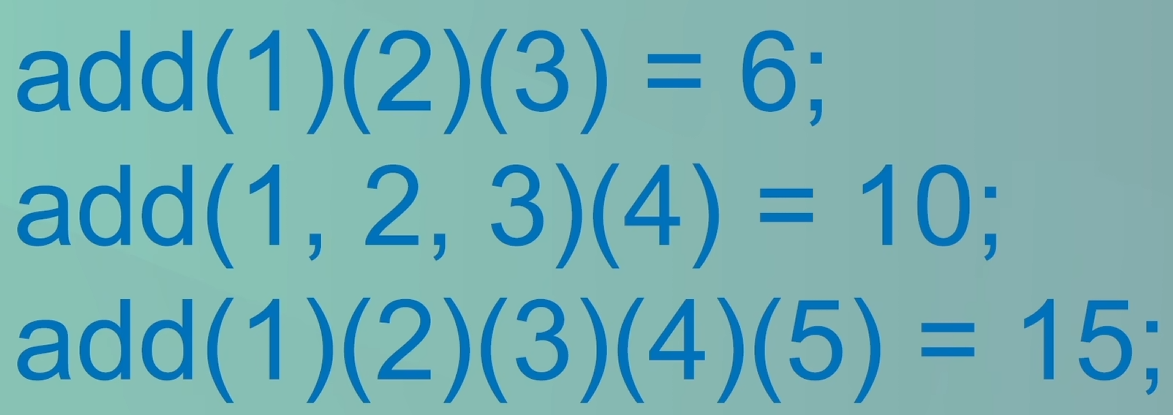
function add(...args){
const sum = args.reduce((total,num)=>total+num,0);
//用curry判断还有没有剩余参数
function curry(...nextArgs){
//闭包,递归的终止条件
//如果没有剩余参数,输出结果
if(nextArgs.length===0){return sum;}
//如果有,则继续加
return add(sum,...nextArgs);
}
return curry;
}
console.log(add(1)(2)(3)()); // 输出: 6
console.log(add(1, 2, 3)(4)()); // 输出: 10
console.log(add(1)(2)(3)(4)(5)()); // 输出: 15
promise.all
要点:
- promise里面不需要return,而是需要resolve和reject
- 如果在Promise.all中的Promise数组中有一个或多个Promise被拒绝(即失败),Promise.all返回的新的Promise会立即被拒绝,并且会传递第一个被拒绝的Promise的错误原因。
思路:for循环遍历所有的promises数组,所有的都成功则resolve,有一个失败则立即reject
function myPromiseAll(promises) { return new Promise((resolve, reject) => { if (!Array.isArray(promises)) { reject(new TypeError("参数必须是一个数组")); } let results = []; if (promises.length === 0) { resolve(results); } for (let promise of promises) { promise .then((res) => { results[results.length] = res; if (results.length === promises.length) { return resolve(results); } }) .catch((error) => { reject(error); }); } }); }Promise.race
要点:
如果在 Promise.race 中的第一个 Promise 对象被拒绝(rejected),则整个 Promise.race 会立即拒绝(reject)并返回该拒绝的原因。后续的 Promise 对象不会再被执行。
function myPromiseRace(promises) { return new Promise((resolve, reject) => { if (!Array.isArray(promises)) { reject(new TypeError("argus must be a array")); } for (let promise of promises) { promise .then((result) => { resolve(result); }) .catch((error) => { reject(error); }); } }); }数组扁平化
方法1:展开数组,层层剥开【推荐】
let arr = [1, [2, [3, 4, 5]]] function flatten2(arr){ while(arr.some((item)=>Array.isArray(item))){ arr = [].concat(...arr) } return arr; } console.log(flatten2(arr));递归写法:
function flat(arr){ arr = [].concat(...arr) if(arr.some((item)=>item instanceof Array)){ arr = flat(arr) } return arr }方法2:判断当前项是否为数组 如果是数组递归调用 不是就push到新数组
function flatten(arr) { let newArr=[]; for(let item of arr){ if(Array.isArray(item)){ newArr = newArr.concat(flatten(item)) }else{ newArr.push(item) } } return newArr; }数组去重
两种方法
function only1(arr){ return arr.filter((value,index)=>{return arr.indexOf(value)===index}) }其中,indexOf 方法会返回指定元素在数组中第一次出现的索引
function only(arr){ return [...new Set(arr)] }实现reduce
array.reduce(callbackfn: (previousValue,currentValue, currentIndex, array), initialValue )
Array.prototype.myReduce = function(callback, initialValue){ //判断参数是否正确 if(typeof callback !=='function'){return new TypeError("callback must be a function")} let accumulator; //检查有没有设置初始值 if(!initialValue){ if(this.length===0){return new TypeError("can't reduce a empty array")} accumulator = this[0] }else{ accumulator = initialValue } //循环调用callback for(let i = initialValue?0:1;i accumulator = callback(accumulator,this[i],i,this) } //返回结果值 return accumulator; } console.log([1,2,3].myReduce((pre,cur)={return pre+cur},0));实现push
Array.prototype.myPush = function(){ for(let i=0;i this[this.length]=arguments[i] } return this.length; } id: 1, pid: 0, name: 'body', }, { id: 2, pid: 1, name: 'title', }, { id: 3, pid: 2, name: 'div', }, { id: 4, pid: 0, name: 'html', }, { id: 5, pid: 4, name: 'div', }, { id: 6, pid: 5, name: 'span', }, { id: 7, pid: 5, name: 'img', }, ][ // 转为 ({ id: 1, pid: 0, name: 'body', children: [ { id: 2, pid: 1, name: 'title', children: [{ id: 3, pid: 2, name: 'div' }], }, ], }, { id: 4, pid: 0, name: 'html', children: [ { id: 5, pid: 4, name: 'div', children: [{ id: 7, pid: 5, name: 'img' }], }, ], }) ] let result = []; for (const item of arr) { if (item.pid === parentId) { item.children = buildTree(arr, item.id); result.push(item); } } return result; } const nodeMap = new Map(); const result = []; arr.forEach((item) = nodeMap.set(item.id, { ...item, children: [] })); for (const item of arr) { if (item.pid === pid) { const children = buildTree(arr, item.id); nodeMap.get(item.id).children = children; result.push(nodeMap.get(item.id)); } } return result; }树转数组
function TreeToArray(arr){ let result = [] for(let item of arr){ if(item.children){ result = result.concat(TreeToArray(item.children)) delete item.children result.push(item) }else{ result.push(item) } } return result; }斐波那契数列的迭代和递归实现
function fiber(n) { if (n >= 0) { if (n == 0) return 0; if (n == 1) return 1; return fiber(n - 1) + fiber(n - 2); } } function fiber2(n){ let F=[] F[0]=0; F[1]=1; for(let i=2;i F[i]=F[i-1]+F[i-2] } console.log(F); return F[n] } setTimeout(()={ console.log(i) },1000*i) } function inside(){ fn() setTimeout(inside,delay); } inside(); } function inside(){ func() setTimeout(inside,delay) } setTimeout(inside,delay); } let timer; function inside(){ func(); timer = setTimeout(inside,delay) } timer = setTimeout(inside,delay) return{ cancel:function(){ clearTimeout(timer); } } }







还没有评论,来说两句吧...