温馨提示:这篇文章已超过448天没有更新,请注意相关的内容是否还可用!
摘要:机械臂的运动学求解包括正向和逆向两个方面。正向运动学求解是通过已知机械臂的关节参数和构型,计算其末端执行器的位置和姿态。逆向运动学求解则是根据末端执行器的期望位置和姿态,反求机械臂的关节参数,以实现精确控制。两者共同构成了机械臂运动控制的基础,对于自动化、机器人等领域具有重要意义。
机械臂的正运动学求解即建立DH参数表,然后计算出各变换矩阵以及最终的变换矩阵。逆运动学求解,即求出机械臂各关节θ角与px,py,pz的关系,建立θ角与末端姿态之间的数学模型,在这里以IRB6700为例,对IRB6700进行正逆运动学求解和验证。
目录
正运动学求解
逆运动学求解
正逆运动学模型的验证
正运动学验证
逆运动学验证
总的Matlab代码,包含正逆运动学求解和验证
参考文献
正运动学求解
首先使用DH法建立坐标系如下:

查阅IRB6700的参数如下表
| 连杆i |
| 关节角 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 780 | +170 —— (-170) | |
| 2 | 320 | -90 | 0 | +85 —— (-65) | |
| 3 | 1125 | 0 | 0 | +70 —— (-180) | |
| 4 | 200 | -90 | 1142.5 | +300 —— (-300) | |
| 5 | 0 | 90 | 0 | +130 —— (-130) | |
| 6 | 0 | -90 | 200 | +360 —— (-360) |
根据变换矩阵公式编写matlab代码计算得到正运动学的各变换矩阵
上式中的为
,
为
,
为
计算变换矩阵的MATLAB代码如下
clear;clc
%%
%导入参数
%注,这里的a,afa的下标在实际使用时均需要减去1
syms a afa d theta [1 6]
a = [0 a2 a3 a4 0 0];
afa = [0 -90 0 -90 90 -90];
d = [d1 0 0 d4 0 d6];
theta = [theta1 theta2 theta3 theta4 theta5 theta6];
syms T [4 4 6]
%%
%正运动学模型求解
%计算各变换矩阵及总的变换矩阵
for i = 1:6
T(:,:,i) = trans_cal( afa(i), a(i), d(i), theta(i)*180/pi );
if(i == 1)
trans_matrix = T(:,:,i);
else
trans_matrix = trans_matrix*T(:,:,i);
end
end
用到的funcion函数如下
function T = trans_cal(afa_ii,a_ii,d_i,theta_i)
%%
%计算变换矩阵函数T_{i-1,i}
%输入的参数为,afa_{i-1},a_{i-1},d_i,theta_i,与DH表达法的参数表对应
%ii 为i-1
%注意,这里输入的角度,均采用角度制,不采用弧度制
T = [cosd(theta_i) -sind(theta_i) 0 a_ii
sind(theta_i)*cosd(afa_ii) cosd(theta_i)*cosd(afa_ii) -sind(afa_ii) -sind(afa_ii)*d_i
sind(theta_i)*sind(afa_ii) cosd(theta_i)*sind(afa_ii) cosd(afa_ii) cosd(afa_ii)*d_i
0 0 0 1 ];
end 各个变换矩阵存储在T中,其中即为变换矩阵
,
存储在trans_matrix中。
逆运动学求解
设总的变换矩阵设为下数:
有等式
根据上面的正运动学求解可以得到矩阵中的等各元素的值分别为什么
使用matlab的实时计算脚本可以较具体地看到

然后通过封闭解法求逆,将上述等式中右边地变换矩阵乘到左边,然后观察等式两边矩阵中地元素,使等式两边的矩阵中的某个元素相等,不断分离变量,然后求解得到
角
首先求解,构造等式

观察等式,使等式两边矩阵的第三行第四列元素相等
上述等式只含有一个未知数,一个等式一个未知数,求解过程如下:
注:为了便于计算,均用
代替,
也用
代替,即下列式子中的
实际上为
,其他的
和
亦然如此

用同样的方式求解

令等式左右两边的第一行第四列,和第三行第四列分别相等,求解过程如下


然后是

令等式两边第一行第四列,第二行第四列相等
求解过程如下:

再然后是的求解

令左右两边第三行第三列相等
求解过程如下

最后是和
的求解
对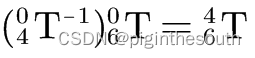 ,使等式左右第一行第三列,和第三行第三列相等
,使等式左右第一行第三列,和第三行第三列相等
对 ,使等式左右第三行第一列,和第三行第二列相等
,使等式左右第三行第一列,和第三行第二列相等
求解过程如下

至此完成了所有角的求解
再次注名:上述推导过程中,为了便于计算,均用
代替,
也用
代替,即上述式子中的
实际上为
,其他的
和
亦然如此
正逆运动学模型的验证
正运动学验证
随机选定一组关节角进行验证,
| 关节角 | ||||||
| 度数 | 22.12 | -81.4 | 21.25 | -84 | 19.14 | 275.13 |
使用之前求解的正运动学模型求解得到末端姿态矩阵如下

使用RobotStudio软件导入IRB6700机器人,输入选择的角
注意:由连杆参数可知,RobotStudio软件中的角度为原角度加上
,
为原角度减去
,所以RobotStudio中输入的角度应如下:
| 关节角 |  得到的TCP末端xyz坐标 对比RobotStudio软件中的末端姿态[x,y,z]值与正解求得的矩阵中末端姿态左边[px,py,pz]可得,两者相等,因此正运动学模型正确。 逆运动学验证由上述的正运动学验证继续计算,上述正运动学得到的末端姿态矩阵如下:
根据此末端姿态矩阵对逆运动学进行求解,可得到八种不同的 求解的matlab代码较长,共一个主m文件,以及5个function文件,放在本文最后。 求解得到共八种组合的
由上表的结果对比可知,除了计算精度问题导致的,部分结果小数点后两位与RobotStudio存在一个单位的差异外,结果一致,因为可以验证逆运动学模型正确。 总的Matlab代码,包含正逆运动学求解和验证clear;clc
%%
%导入参数
%注,这里的a,afa的下标在实际使用时均需要减去1
syms a afa d theta [1 6]
a = [0 a2 a3 a4 0 0];
afa = [0 -90 0 -90 90 -90];
d = [d1 0 0 d4 0 d6];
theta = [theta1 theta2 theta3 theta4 theta5 theta6];
syms T [4 4 6]
%%
%正运动学模型求解
%计算各变换矩阵及总的变换矩阵
for i = 1:6
T(:,:,i) = trans_cal( afa(i), a(i), d(i), theta(i)*180/pi );
if(i == 1)
trans_matrix = T(:,:,i);
else
trans_matrix = trans_matrix*T(:,:,i);
end
end
%%
%逆运动学计算求解
syms r [3 3]
syms PX_X PY_Y PZ_Z
T_60 = [r1_1 r1_2 r1_3 PX_X;
r2_1 r2_2 r2_3 PY_Y;
r3_1 r3_2 r3_3 PZ_Z;
0 0 0 1];
left_1 = simplify( inv( T(:,:,2) ) * inv( T(:,:,1) ) * T_60 * inv( T(:,:,6) ) );
right_1 = simplify( T(:,:,3)*T(:,:,4)*T(:,:,5) );
left_2 = simplify( inv( T(:,:,1) )* T_60 * inv( T(:,:,6) ) );
right_2 = simplify( T(:,:,2)*T(:,:,3)*T(:,:,4)*T(:,:,5) );
left_3 = simplify( inv( T(:,:,1)*T(:,:,2) ) * T_60 * inv( T(:,:,6) ) );
right_3 = simplify( T(:,:,3)*T(:,:,4)*T(:,:,5) );
left_4 = simplify( inv( T(:,:,1)*T(:,:,2)*T(:,:,3)*T(:,:,4)*T(:,:,5) ) * T_60 );
right_4 = simplify( T(:,:,6) );
left_5 = simplify( inv( T(:,:,1)*T(:,:,2)*T(:,:,3)*T(:,:,4) ) * T_60 );
right_5 = simplify( T(:,:,5)*T(:,:,6) );
left_6 = simplify( inv( T(:,:,1)*T(:,:,2)*T(:,:,3)*T(:,:,4)*T(:,:,5) ) * T_60 );
right_6 = simplify( T(:,:,6) );
%%
%逆运动学验算
%末端姿态
T_ni = [-0.5 0 0.866 1635.672;
0 1 0 594.531;
-0.866 0 -0.5 1396.902;
0 0 0 1];
r1_1 = T_ni(1,1);r1_2 = T_ni(1,2);r1_3 = T_ni(1,3);PX_X = T_ni(1,4);
r2_1 = T_ni(2,1);r2_2 = T_ni(2,2);r2_3 = T_ni(2,3);PY_Y = T_ni(2,4);
r3_1 = T_ni(3,1);r3_2 = T_ni(3,2);r3_3 = T_ni(3,3);PZ_Z = T_ni(3,4);
syms a d [1 6]
d1 = 780;d4 = 1142.5;d6 = 200;
a2 = 320;a3 = 1125 ;a4 = 200;
syms A B C D E F [1 6]
%theta1的解
theta1_1 = ( atan2(0,1) - atan2( d6*r2_3-PY_Y , PX_X-d6*r1_3 ) )*180/pi %22.1230
theta1_2 = ( -atan2(0,-1) - atan2( d6*r2_3-PY_Y , PX_X-d6*r1_3 ) )*180/pi %-157.8770
%theta2的解
[theta2_1 , theta2_2] = theta2_calculate(theta1_1) %theta1为22.123°时
[theta2_3 , theta2_4] = theta2_calculate(theta1_2) %theta1为-157.8770°时
%theta3的解
theta3_11_21 = theta3_calculate(theta1_1,theta2_1) %theta1为22.123°theta2为-81.3955°时
theta3_11_22 = theta3_calculate(theta1_1,theta2_2) %theta1为22.123°theta2为22.0674°时
theta3_12_23 = theta3_calculate(theta1_2,theta2_3) %theta1为-157.8770°theta2为172.8834°时
theta3_12_24 = theta3_calculate(theta1_2,theta2_4) %theta1为-157.8770°theta2为228.4872°时
%theta4的解
[theta4_1_11_21,theta4_2_11_21] = theta4_calculate(theta1_1,theta2_1,theta3_11_21) %theta1为22.123°theta2为-81.3955°时
[theta4_1_11_22,theta4_2_11_22] = theta4_calculate(theta1_1,theta2_2,theta3_11_22) %theta1为22.123°theta2为22.0674°时
[theta4_1_12_23,theta4_2_12_23] = theta4_calculate(theta1_2,theta2_3,theta3_12_23) %theta1为-157.8770°theta2为172.8834°时
[theta4_1_12_24,theta4_2_12_24] = theta4_calculate(theta1_2,theta2_4,theta3_12_24) %theta1为-157.8770°theta2为228.4872°时
%theta5的解
theta5_11_21_41 = theta5_calculate(theta1_1,theta2_1,theta3_11_21,theta4_1_11_21) %theta1为22.123°theta2为-81.3955°,theta4为第1种
theta5_11_21_42 = theta5_calculate(theta1_1,theta2_1,theta3_11_21,theta4_2_11_21) %theta1为22.123°theta2为-81.3955°,theta4为第2种
theta5_11_22_41 = theta5_calculate(theta1_1,theta2_2,theta3_11_22,theta4_1_11_22) %theta1为22.123°theta2为22.0674°,theta4为第1种
theta5_11_22_42 = theta5_calculate(theta1_1,theta2_2,theta3_11_22,theta4_2_11_22) %theta1为22.123°theta2为22.0674°,theta4为第2种
theta5_12_23_41 = theta5_calculate(theta1_2,theta2_3,theta3_12_23,theta4_1_12_23) %theta1为-157.8770°theta2为172.8834°,theta4为第1种
theta5_12_23_42 = theta5_calculate(theta1_2,theta2_3,theta3_12_23,theta4_2_12_23) %theta1为-157.8770°theta2为172.8834°,theta4为第2种
theta5_12_24_41 = theta5_calculate(theta1_2,theta2_4,theta3_12_24,theta4_1_12_24) %theta1为-157.8770°theta2为228.4872°,theta4为第1种
theta5_12_24_42 = theta5_calculate(theta1_2,theta2_4,theta3_12_24,theta4_2_12_24) %theta1为-157.8770°theta2为228.4872°,theta4为第2种
% theta6的解
theta6_11_21_41 = theta6_calculate(theta1_1,theta2_1,theta3_11_21,theta4_1_11_21) %theta1为22.123°theta2为-81.3955°,theta4为第1种
theta6_11_21_42 = theta6_calculate(theta1_1,theta2_1,theta3_11_21,theta4_2_11_21) %theta1为22.123°theta2为-81.3955°,theta4为第2种
theta6_11_22_41 = theta6_calculate(theta1_1,theta2_2,theta3_11_22,theta4_1_11_22) %theta1为22.123°theta2为22.0674°,theta4为第1种
theta6_11_22_42 = theta6_calculate(theta1_1,theta2_2,theta3_11_22,theta4_2_11_22) %theta1为22.123°theta2为22.0674°,theta4为第2种
theta6_12_23_41 = theta6_calculate(theta1_2,theta2_3,theta3_12_23,theta4_1_12_23) %theta1为-157.8770°theta2为172.8834°,theta4为第1种
theta6_12_23_42 = theta6_calculate(theta1_2,theta2_3,theta3_12_23,theta4_2_12_23) %theta1为-157.8770°theta2为172.8834°,theta4为第2种
theta6_12_24_41 = theta6_calculate(theta1_2,theta2_4,theta3_12_24,theta4_1_12_24) %theta1为-157.8770°theta2为228.4872°,theta4为第1种
theta6_12_24_42 = theta6_calculate(theta1_2,theta2_4,theta3_12_24,theta4_2_12_24) %theta1为-157.8770°theta2为228.4872°,theta4为第2种
function [theta2_1,theta2_2] = theta2_calculate(theta1)
%%
%导入参数
syms r [3,3]
syms a afa d
syms PX_X PY_Y_Y PZ_Z
T_ni = [-0.5 0 0.866 1635.672;
0 1 0 594.531;
-0.866 0 -0.5 1396.902;
0 0 0 1];
r1_1 = T_ni(1,1);r1_2 = T_ni(1,2);r1_3 = T_ni(1,3);PX_X = T_ni(1,4);
r2_1 = T_ni(2,1);r2_2 = T_ni(2,2);r2_3 = T_ni(2,3);PY_Y = T_ni(2,4);
r3_1 = T_ni(3,1);r3_2 = T_ni(3,2);r3_3 = T_ni(3,3);PZ_Z = T_ni(3,4);
syms a d [1 6]
d1 = 780;d4 = 1142.5;d6 = 200;
a2 = 320;a3 = 1125 ;a4 = 200;
syms A B C D E F [1 6]
theta1 = theta1/180*pi;
%%
%theta2计算
A2 = ( PX_X - d6*r1_3 )*cos(theta1) + ( PY_Y - d6*r2_3 )*sin(theta1) - a2;
B2 = d1 + d6*r3_3 - PZ_Z;
C2 = 2*A2*a3;
D2 = 2*B2*a3;
E2 = A2^2 + B2^2 + a3^2 - a4^2 - d4^2;
F2 = sqrt( C2^2 + D2^2 );
theta2_1 = ( -atan2(C2,D2) + atan2( E2/F2 , sqrt( 1- (E2/F2)^2 ) ) )*180/pi ;
theta2_2 = ( -atan2(C2,D2) + atan2( E2/F2 , -sqrt( 1- (E2/F2)^2 ) ) )*180/pi ;
end function theta3 = theta3_calculate(theta1,theta2)
%%
%导入参数
syms r [3,3]
syms a afa d
syms PX_X PY_Y_Y PZ_Z
T_ni = [-0.5 0 0.866 1635.672;
0 1 0 594.531;
-0.866 0 -0.5 1396.902;
0 0 0 1];
r1_1 = T_ni(1,1);r1_2 = T_ni(1,2);r1_3 = T_ni(1,3);PX_X = T_ni(1,4);
r2_1 = T_ni(2,1);r2_2 = T_ni(2,2);r2_3 = T_ni(2,3);PY_Y = T_ni(2,4);
r3_1 = T_ni(3,1);r3_2 = T_ni(3,2);r3_3 = T_ni(3,3);PZ_Z = T_ni(3,4);
syms a d [1 6]
d1 = 780;d4 = 1142.5;d6 = 200;
a2 = 320;a3 = 1125 ;a4 = 200;
syms A B C D E F [1 6]
theta1 = theta1/180*pi;
theta2 = theta2/180*pi;
%%
%theta3计算
A3 = d1*sin(theta2) - a2*cos(theta2) - PZ_Z*sin(theta2) + d6*r3_3*sin(theta2) + PX_X*cos(theta1)*cos(theta2) ...
+ PY_Y*cos(theta2)*sin(theta1) - d6*r1_3*cos(theta1)*cos(theta2) - d6*r2_3*cos(theta2)*sin(theta1) - a3;
B3 = d1*cos(theta2) - PZ_Z*cos(theta2) + a2*sin(theta2) + d6*r3_3*cos(theta2) - PX_X*cos(theta1)*sin(theta2) ...
- PY_Y*sin(theta1)*sin(theta2) + d6*r2_3*sin(theta1)*sin(theta2) + d6*r1_3*cos(theta1)*sin(theta2);
C3 = ( a4*B3-d4*A3 ) / ( a4^2 + d4^2 );
D3 = ( a4*A3+d4*B3 ) / ( a4^2 + d4^2 );
theta3 = atan2( C3,D3 )*180/pi;
end function [theta4_1,theta4_2] = theta4_calculate(theta1,theta2,theta3)
%%
%导入参数
syms r [3,3]
syms a afa d
syms PX_X PY_Y_Y PZ_Z
T_ni = [-0.5 0 0.866 1635.672;
0 1 0 594.531;
-0.866 0 -0.5 1396.902;
0 0 0 1];
r1_1 = T_ni(1,1);r1_2 = T_ni(1,2);r1_3 = T_ni(1,3);PX_X = T_ni(1,4);
r2_1 = T_ni(2,1);r2_2 = T_ni(2,2);r2_3 = T_ni(2,3);PY_Y = T_ni(2,4);
r3_1 = T_ni(3,1);r3_2 = T_ni(3,2);r3_3 = T_ni(3,3);PZ_Z = T_ni(3,4);
syms a d [1 6]
d1 = 780;d4 = 1142.5;d6 = 200;
a2 = 320;a3 = 1125 ;a4 = 200;
syms A B C D E F [1 6]
theta1 = theta1/180*pi;
theta2 = theta2/180*pi;
theta3 = theta3/180*pi;
%%
%theta4计算
A4 = r3_3*cos(theta2)*sin(theta3) + r3_3*cos(theta3)*sin(theta2) - r1_3*cos(theta1)*cos(theta2)*cos(theta3) ...
- r2_3*cos(theta2)*cos(theta3)*sin(theta1) + r1_3*cos(theta1)*sin(theta2)*sin(theta3) ...
+ r2_3*sin(theta1)* sin(theta2)*sin(theta3);
B4 = r2_3*cos(theta1) - r1_3*sin(theta1);
theta4_1 = ( atan2( 0,1 ) + atan2( B4,A4 ) )*180/pi;
theta4_2 = ( atan2( 0,-1 ) + atan2( B4,A4 ) )*180/pi;
end function theta5 = theta5_calculate(theta1,theta2,theta3,theta4)
%%
%导入参数
syms r [3,3]
syms a afa d
syms PX_X PY_Y_Y PZ_Z
T_ni = [-0.5 0 0.866 1635.672;
0 1 0 594.531;
-0.866 0 -0.5 1396.902;
0 0 0 1];
r1_1 = T_ni(1,1);r1_2 = T_ni(1,2);r1_3 = T_ni(1,3);PX_X = T_ni(1,4);
r2_1 = T_ni(2,1);r2_2 = T_ni(2,2);r2_3 = T_ni(2,3);PY_Y = T_ni(2,4);
r3_1 = T_ni(3,1);r3_2 = T_ni(3,2);r3_3 = T_ni(3,3);PZ_Z = T_ni(3,4);
syms a d [1 6]
d1 = 780;d4 = 1142.5;d6 = 200;
a2 = 320;a3 = 1125 ;a4 = 200;
syms A B C D E F [1 6]
theta1 = theta1/180*pi;
theta2 = theta2/180*pi;
theta3 = theta3/180*pi;
theta4 = theta4/180*pi;
%%
%theta4计算
A5 = r1_3*sin(theta1)*sin(theta4) - r2_3*cos(theta1)*sin(theta4) - r3_3*cos(theta2)*cos(theta4)*sin(theta3) ...
- r3_3*cos(theta3)*cos(theta4)*sin(theta2) + r1_3*cos(theta1)*cos(theta2)*cos(theta3)*cos(theta4) + ...
r2_3*cos(theta2)*cos(theta3)*cos(theta4)*sin(theta1) - r1_3*cos(theta1)*cos(theta4)*sin(theta2)*sin(theta3) ...
- r2_3*cos(theta4)*sin(theta1)*sin(theta2)*sin(theta3);
B5 = r3_3*sin(theta2)*sin(theta3) - r3_3*cos(theta2)*cos(theta3) - r1_3*cos(theta1)*cos(theta2)*sin(theta3) ...
- r1_3*cos(theta1)*cos(theta3)*sin(theta2) - r2_3*cos(theta2)*sin(theta1)*sin(theta3) - ...
r2_3*cos(theta3)*sin(theta1)*sin(theta2);
theta5 = atan2(-A5,B5)*180/pi;
end function theta6 = theta6_calculate(theta1,theta2,theta3,theta4)
%%
%导入参数
syms r [3,3]
syms a afa d
syms PX_X PY_Y_Y PZ_Z
T_ni = [-0.5 0 0.866 1635.672;
0 1 0 594.531;
-0.866 0 -0.5 1396.902;
0 0 0 1];
r1_1 = T_ni(1,1);r1_2 = T_ni(1,2);r1_3 = T_ni(1,3);PX_X = T_ni(1,4);
r2_1 = T_ni(2,1);r2_2 = T_ni(2,2);r2_3 = T_ni(2,3);PY_Y = T_ni(2,4);
r3_1 = T_ni(3,1);r3_2 = T_ni(3,2);r3_3 = T_ni(3,3);PZ_Z = T_ni(3,4);
syms a d [1 6]
d1 = 780;d4 = 1142.5;d6 = 200;
a2 = 320;a3 = 1125 ;a4 = 200;
syms A B C D E F [1 6]
theta1 = theta1/180*pi;
theta2 = theta2/180*pi;
theta3 = theta3/180*pi;
theta4 = theta4/180*pi;
%%
%theta4计算
A6 = r2_1*cos(theta1)*cos(theta4) - r1_1*cos(theta4)*sin(theta1) - r3_1*cos(theta2)*sin(theta3)*sin(theta4) ...
- r3_1*cos(theta3)*sin(theta2)*sin(theta4) + r1_1*cos(theta1)*cos(theta2)*cos(theta3)*sin(theta4) + ...
r2_1*cos(theta2)*cos(theta3)*sin(theta1)*sin(theta4) - r1_1*cos(theta1)*sin(theta2)*sin(theta3)*sin(theta4) ...
- r2_1*sin(theta1)*sin(theta2)*sin(theta3)*sin(theta4);
B6 = r2_2*cos(theta1)*cos(theta4) - r1_2*cos(theta4)*sin(theta1) - r3_2*cos(theta2)*sin(theta3)*sin(theta4) ...
- r3_2*cos(theta3)*sin(theta2)*sin(theta4) + r1_2*cos(theta1)*cos(theta2)*cos(theta3)*sin(theta4) ...
+ r2_2*cos(theta2)*cos(theta3)*sin(theta1)*sin(theta4) - r1_2*cos(theta1)*sin(theta2)*sin(theta3)*sin(theta4) ...
- r2_2*sin(theta1)*sin(theta2)*sin(theta3)*sin(theta4);
theta6 = atan2(-A6,-B6)*180/pi;
end function T = trans_cal(afa_ii,a_ii,d_i,theta_i)
%%
%计算变换矩阵函数T_{i-1,i}
%输入的参数为,afa_{i-1},a_{i-1},d_i,theta_i,与DH表达法的参数表对应
%ii 为i-1
%注意,这里输入的角度,均采用角度制,不采用弧度制
T = [cosd(theta_i) -sind(theta_i) 0 a_ii
sind(theta_i)*cosd(afa_ii) cosd(theta_i)*cosd(afa_ii) -sind(afa_ii) -sind(afa_ii)*d_i
sind(theta_i)*sind(afa_ii) cosd(theta_i)*sind(afa_ii) cosd(afa_ii) cosd(afa_ii)*d_i
0 0 0 1 ];
end 参考文献[1] 尹绪伟. 打磨机器人不同位姿下的刚度特性研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2019. [2] 王宇迪. 基于加工姿态最优的发动机飞轮壳机器人铣削修边空间路径规划[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2022. 相关阅读: 1、网站SSL证书出现错误和解决过程,网站SSL证书错误及解决流程 2、替换FeedBurner邮件为Follow.it,FeedBurner邮件替换为Follow.it,全新邮件订阅体验 3、使用正则表达式进行中文排版,使用正则表达式进行中文排版的技巧与方法 文章版权声明:除非注明,否则均为VPS857原创文章,转载或复制请以超链接形式并注明出处。 相关阅读发表评论 |







还没有评论,来说两句吧...