温馨提示:这篇文章已超过468天没有更新,请注意相关的内容是否还可用!
摘要:本文介绍了Android系统中与T WMS窗口相关的流程。这些流程涉及T WMS窗口的创建、显示、管理和交互等方面。通过优化这些流程,可以提高Android系统的性能和用户体验,包括响应速度、界面流畅度和资源利用率等。对于开发者而言,了解这些流程有助于更好地集成和定制T WMS窗口,以满足不同应用的需求。
文章目录
- 一、介绍
- 二、流程简述
- 1.客户端
- 2. 通信方式
- 3. 服务端
- 3.1.addWindow
- 3.2 relayoutWindow
- 3.3 finishDrawingWindow
- 4.窗口状态变化总结
- 5.移除流程简述
- 三、代码流程详解
- 1.客户端
- 1.1 Activity走到onresume后
- 1.2 Token的创建与传递
- 1.3 ViewRootImpl的创建
- 1.4 ViewRootImpl与WMS的通信
- 2.服务端
- 2.1 窗口添加
- 2.1.1 接收客户端请求
- 2.1.2 addWindow
- 2.1.3 WindowToken的创建
- 2.1.4 WindowState初始化
- 2.1.5 将WindowState加入到WindowToken
- 2.2 窗口位置和大小计算
- 2.2.1 接收客户端请求
- 2.2.2 relayoutWindow
- 2.2.3 创建SurfaceControl
- 2.2.4 计算窗口大小位置
- 1.处理窗口布局循环
- 2.处理所有Surface的状态变更,以及调用layoutWindowLw的流程
- 3.计算窗口位置大小
- 2.3 窗口状态刷新
- 2.3.1 接受客户端请求
- 2.3.2 finishDrawingWindow
- 1.mDrawState的状态更变
- 2.请求布局刷新
- * 窗口位置计算与窗口状态刷新流程不同点
- 2.3.3 mDrawState变更为HAS_DRAW
- 1.mApplySurfaceChangesTransaction
- 2.checkAppTransitionReady()
- 3.再次请求布局
- 2.3.4 show Surface
- 2.4 performSurfacePlacement()流程总结
一、介绍
什么是窗口
窗口即是屏幕上的一块用于绘制各种UI元素并可以响应用户输入的一个矩形区域。从原理上讲,窗口的概念是独自占有一个Surface实例的显示区域(我们在屏幕上看到的图形都需要绘制在Surface上)。
Window是个抽象类其实现类为PhoneWindow。
本文以窗口添加的流程为例,讲解窗口添加相关的流程及其涉及的方法。
其他建议:可以先学习层级结构树相关内容,有助于对窗口模块的理解
Android T 窗口层级其一 —— 容器类
Android T 窗口层级其二 —— 层级结构树的构建
Android T 窗口层级其三 —— 层级结构树添加窗口
二、流程简述
当Activity.onResume()被调用之后,客户端会与WMS进行通信将我们的布局显示在屏幕上。其中主要涉及以下几个过程:
客户端通知WMS创建一个窗口,并添加到WindowToken。即addToDisplayAsUser阶段。
客户端通知WMS创建Surface,并计算窗口尺寸大小。即relayoutWindow阶段。
客户端获取到WMS计算的窗口大小后,进一步测量该窗口下View的宽度和高度。即performMeasure阶段。
客户端确定该窗口下View的尺寸和位置。即performLayout阶段。
确定好View的尺寸大小位置之后,便对View进行绘制。即performDraw阶段。
通知WMS,客户端已经完成绘制。WMS进行系统窗口的状态刷新以及动画处理,并最终将Surface显示出来。即reportDrawFinished阶段。
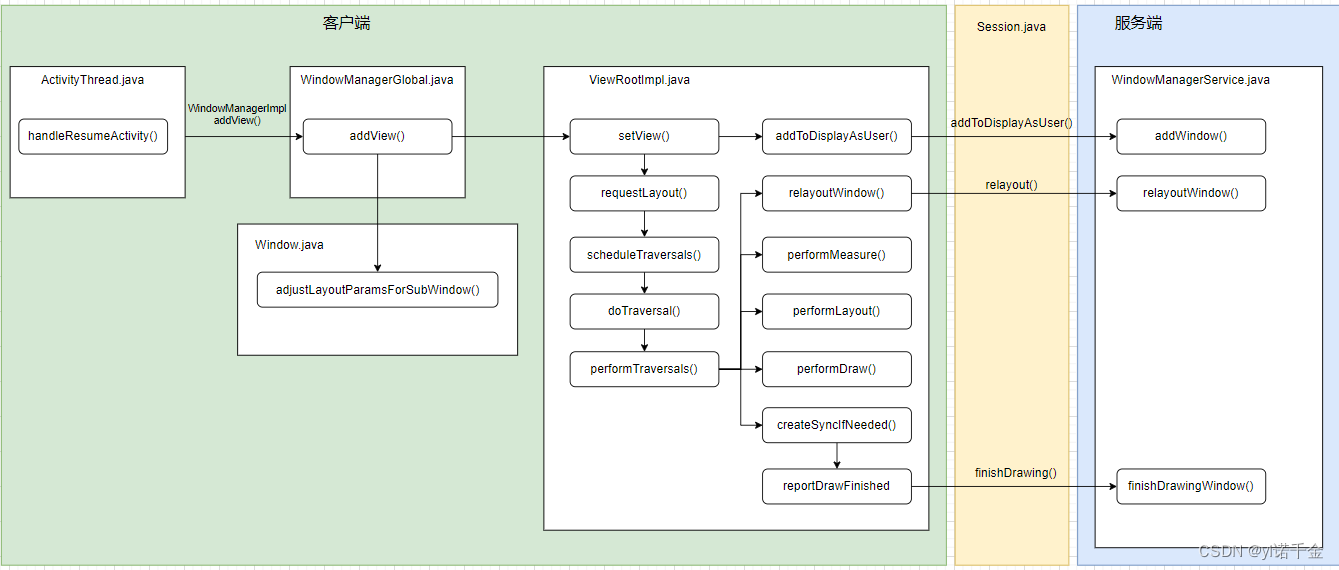
这里以Activity.onResume()被调用之后为起点
1.客户端
WindowManager:是一个接口类,负责窗口的管理(增、删、改)。
WindowManagerImpl:WindowManager的实现类,但是他把对于窗口的具体管理操作交给WindowManagerGlobal来处理。
WindowManagerGlobal:是一个单例类,实现了窗口的添加、删除、更新的逻辑,但是
ViewRootImpl:通过IWindowSession与WMS进行通信。其内部类W实现了WMS与ViewRootImpl的通信。
ActivityThread.java
- handleResumeActivity
通过WindowManager接口添加view,即wm.addView(decor, l);,wm为ViewManager对象,即ViewManager wm = a.getWindowManager();
WindowManagerImpl.java
- addView
mGlobal.addView(view, params, mContext.getDisplayNoVerify(), mParentWindow,mContext.getUserId());mGlobal为WindowManagerGlobal对象。
WindowManagerGlobal.java
- addView
root.setView(view, wparams, panelParentView, userId);root为ViewRootImpl对象。
parentWindow.adjustLayoutParamsForSubWindow(wparams);parentWindow为Window(Window为抽象类,PhoneWindow继承于Window),即在Window中调用adjustLayoutParamsForSubWindow,用于赋值参数布局的token以及title
ViewRootImpl.java
- setView
1.addToDisplayAsUser
客户端通知WMS创建一个窗口,并添加到WindowToken
res = mWindowSession.addToDisplayAsUser(mWindow,mWindowAttributes,getHostVisibility(), mDisplay.getDisplayId(), userId,mInsetsController.getRequestedVisibilities(), inputChannel, mTempInsets,mTempControls);
2.requestLayout
在添加到窗口管理器之前安排第一个布局,以确保我们在从系统接收任何其他事件之前进行重新布局
scheduleTraversals->doTraversal->performTraversals
performTraversals中调用了五个关键方法:
relayoutWindow
客户端通知WMS创建Surface,并计算窗口尺寸大小
performMeasure
客户端获取到WMS计算的窗口大小后,进一步测量该窗口下View的宽度和高度
performLayout
客户端确定该窗口下View的尺寸和位置
performDraw
确定好View的尺寸大小位置之后,便对View进行绘制
createSyncIfNeeded->reportDrawFinished
通知WMS,客户端已经完成绘制。WMS进行系统窗口的状态刷新以及动画处理,并最终将Surface显示出来
2. 通信方式
Session表示一个客户端和服务端的交互会话。一般来说不同的应用通过不同的会话来和WindowManagerService交互,但是处于同一个进程的不同应用通过同一个Session来交互。
IWindowSession.aidl
ViewRootImpl中通过此接口调用服务端
1.addToDisplayAsUser
2.relayout
3.finishDrawing
Session.java
IWindowSession的实现在这里,最终调用到WMS中
1.addToDisplayAsUser->addWindow
2.relayout->relayoutWindow
3.finishDrawing->finishDrawingWindow
3. 服务端
WindowManagerService:负责为Activity对应的窗口分配Surface,管理Surface的显示顺序以及位置尺寸,控制窗口动画,并且还是输入系统的一个重要中转站。
WindowState:和客户端窗口一一对应,在向WMS添加一个窗口时,WMS会为其创建一个WindowState,来表示窗口的所有属性,WindowState相当于属性窗口管理(比如对外提供操作接口,属于层级结构中最底部的容器),窗口画面相关都剥离给了WindowStateAnimator,WindowState也是WMS中事实上的窗口。
WindowStateAnimator:主要用于管理WindowState相关画面surface,通过mDrawState参数来描述Surface所处的状态。
WindowToken:保存了所有具有同一个token的WindowState,将属于同一个activity的窗口组织在一起,activity在需要更新窗口时,必须向WMS提供WindowToken以表名自己的身份,并且窗口的类型必须与所持有的的WindowToken类型一致。
补充:一个WindowToken可以对应多个WindowState。 WindowToken是一个用于表示窗口层次结构中的窗口的标识符。每个Window具有一个与之关联的WindowToken,它用于帮助系统管理窗口的显示和交互。
一个WindowToken可以有多个WindowState表示与之相关的窗口。这是因为在Android系统中,可能会存在一些特殊情况,例如PopupWindow、Dialog等,它们属于同一个WindowToken,但是显示在不同的窗口上。
因此,一个WindowToken可以与多个WindowState关联,这样可以实现多个窗口的操作和管理。
WindowSurfaceController:用来创建SurfaceControl。
DisplayContent:即代表的是单个屏幕。隶属于同一个DisplayContent的窗口将会被显示在同一个屏幕中。每个DisplayContent都对应着一个唯一的id,在添加窗口时可以通过指定这个ID决定将其显示在哪个屏幕中。
WindowSurfacePlacer:整个窗口层次结构刷新的入口。
RootWindowContainer:是窗口容器的顶层容器,其直接管理DisplayContent。
WindowManagerService.java
3.1.addWindow
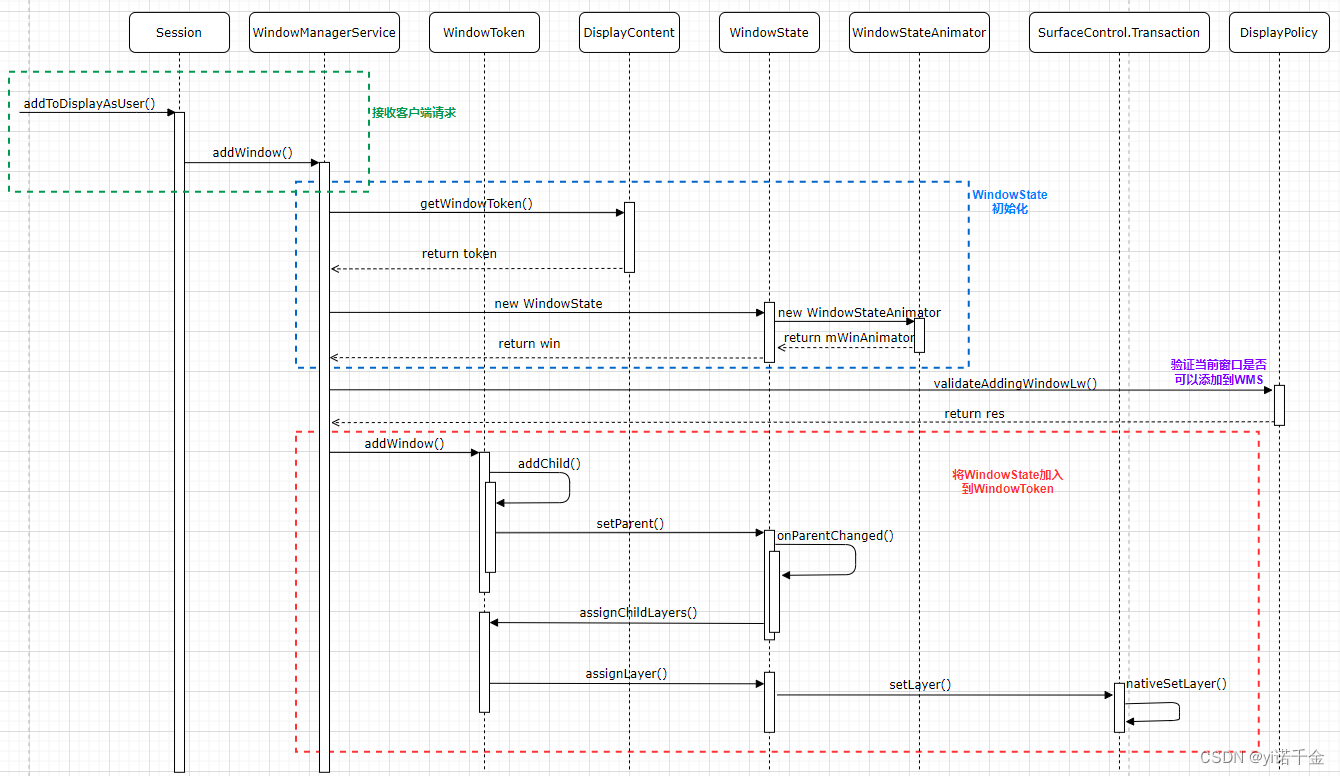
1.根据客户端传来的token获取WindowToken或创建WindowToken,并将其挂载到对应的层级节点上
WindowToken token = displayContent.getWindowToken(hasParent ? parentWindow.mAttrs.token : attrs.token);
判断WindowToken是否有父亲,即parentWindow 是否不为空
final boolean hasParent = parentWindow != null;
注:前面代码有判断是否是子窗口,是则会给parentWindow 赋值;否则parentWindow仍为初始值,即为空
关于窗口类型,见 窗口常见参数汇总
Activity启动时会在ActivityRecord的构造方法中new Token()。
应用侧直接通过addView的方式添加窗口不会有ActivityRecord,因此不会在ActivityRecord的构造方法中new Token()。
系统侧直接添加的窗口(状态栏、导航栏等),是通过new WindowToken.Builder的方式添加
即主动使用ViewManager.addView来添加一个窗口则不会在ActivityRecord的构造方法中new Token(),否则通过new WindowToken.Builder的方式添加。
attrs.token这个参数一可以在应用端设置,应用没有设置token那么就为空,token为IBinder类型对象,默认值为空public IBinder token = null;
例如:
在应用侧可通过mLayoutParams.token的方式设置值
private WindowManager.LayoutParams mLayoutParams;
mLayoutParams.token = null;
后面会继续判断token是否为空,最终会到最后的else中创建token
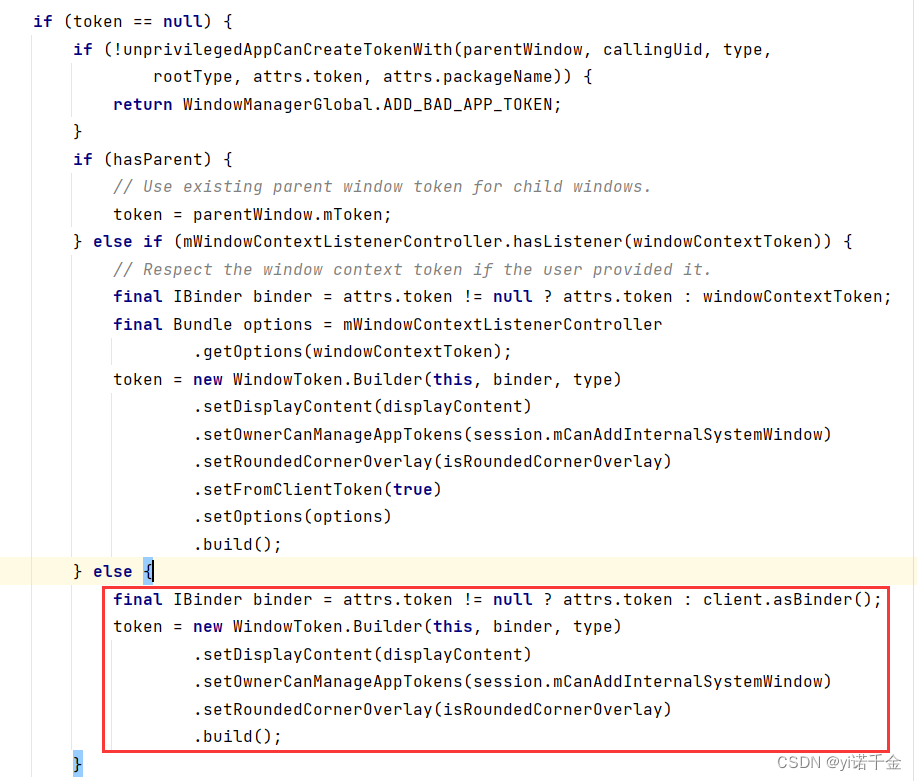
2.创建WindowState
final WindowState win = new WindowState(this, session, client, token, parentWindow, appOp[0], attrs, viewVisibility, session.mUid, userId,session.mCanAddInternalSystemWindow);
3.验证当前窗口是否可以添加到WMS
res = displayPolicy.validateAddingWindowLw(attrs, callingPid, callingUid);
该方法会对窗口TYPE,FLAG等多方面判断。只有返回ADD_OKAY时表示允许当前窗口的添加,反之则不允许添加该窗口。假如想禁止某些应用做添加窗口操作时,可以在里面通过应用的包名过滤该应用,也可以直接在WindowManagerGlobal.java的addView()方法中直接对应用想要添加的窗口进行过滤。
注:ADD_OKAY在WindowManagerGlobal中定义,这个类里面还有一些其他的返回值,所有返回给res的常量最终会在ViewRootImpl的setView方法中判断
4.调用openInputChannel,初始化input相关通路(本文不做讨论)
final boolean openInputChannels = (outInputChannel != null && (attrs.inputFeatures & INPUT_FEATURE_NO_INPUT_CHANNEL) == 0);
if (openInputChannels) { win.openInputChannel(outInputChannel); }
5.将WindowState加入到WindowToken
win.mToken.addWindow(win);
WMS窗口添加之后,还没有创建Surface,此时mDrawState状态为NO_SURFACE
3.2 relayoutWindow
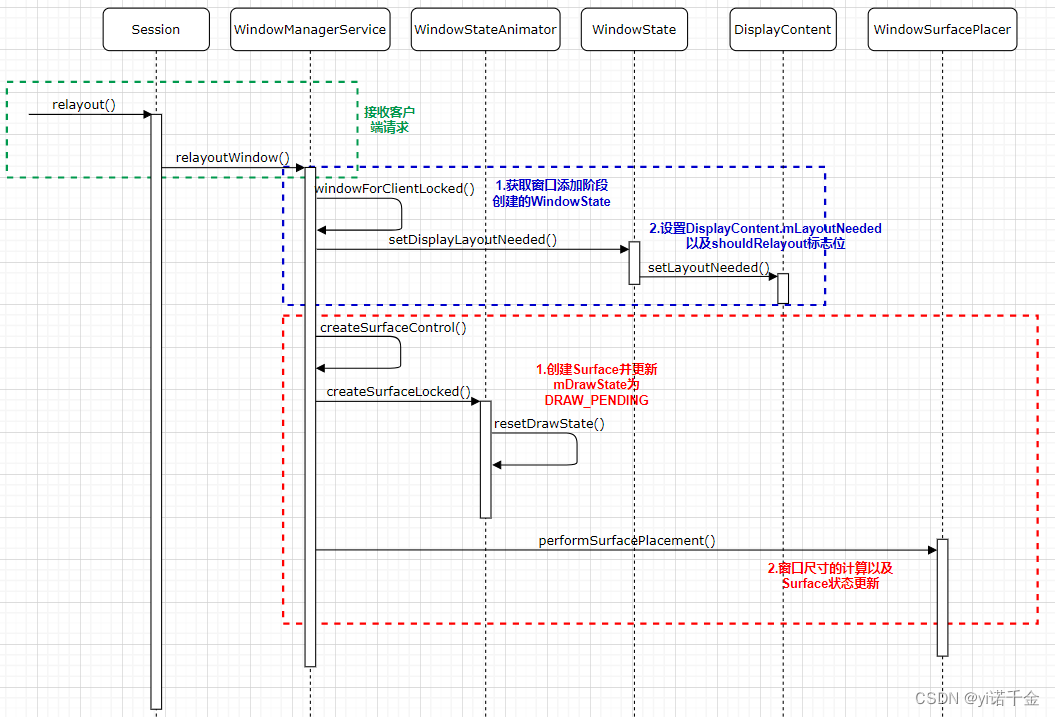
1.根据客户端传递过来的IWindow的mWindowMap获取窗口添加阶段创建的WindowState
final WindowState win = windowForClientLocked(session, client, false);
2.设置DisplayContent.mLayoutNeeded以及shouldRelayout标志位
win.setDisplayLayoutNeeded();win为WindowState对象,该方法实际操作在DisplayContent中
final boolean shouldRelayout = viewVisibility == View.VISIBLE &&(win.mActivityRecord == null || win.mAttrs.type == TYPE_APPLICATION_STARTING || win.mActivityRecord.isClientVisible());
3.创建SurfaceControl
在layoutWindow()调用了createSurfaceControl方法创建SurfaceControl
result = createSurfaceControl(outSurfaceControl, result, win, winAnimator);该方法的实现仍然在WMS中
这里以createSurfaceControl方法为起点
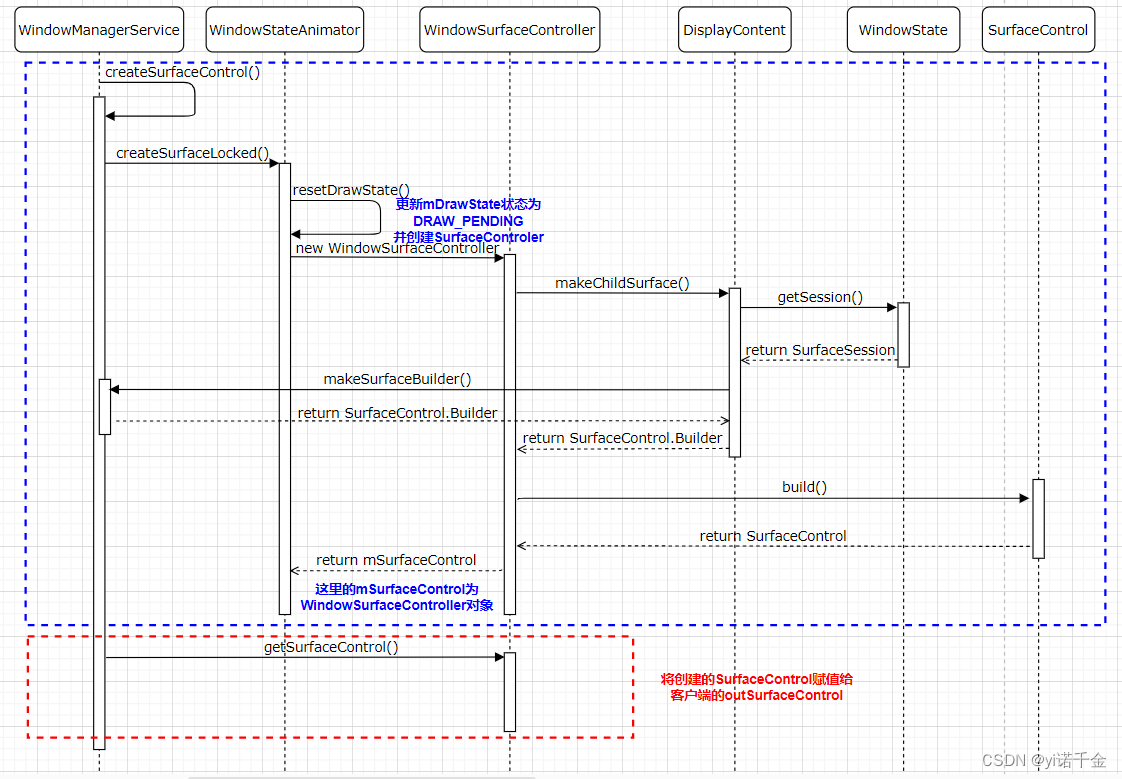
在createSurfaceControl()中调用WindowStateAnimator执行具体的SurfaceControl的创建 surfaceController = winAnimator.createSurfaceLocked();
创建Surface后,Surface还未进行绘制,此时mDrawState状态为DRAW_PENDING
将创建的SurfaceControl赋值给客户端的outSurfaceControl
surfaceController.getSurfaceControl(outSurfaceControl);
4.窗口尺寸的计算以及Surface状态更新
在layoutWindow()调用了performSurfacePlacement
mWindowPlacerLocked.performSurfacePlacement(true /* force */);mWindowPlacerLocked为WindowSurfacePlacer对象,因此这里以WindowSurfacePlacer的performSurfacePlacement()为起点

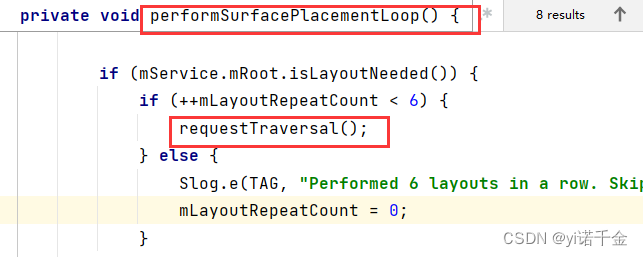
处理窗口布局循环
WindowSurfacePlacer.performSurfacePlacementLoop()
处理Surface的状态更变,以及调用LayoutWindowLw的流程
RootWindowContainer.performSurfacePlacementNoTrace()
计算窗口位置大小
DisplayPolicy.layoutWindowLw()
3.3 finishDrawingWindow
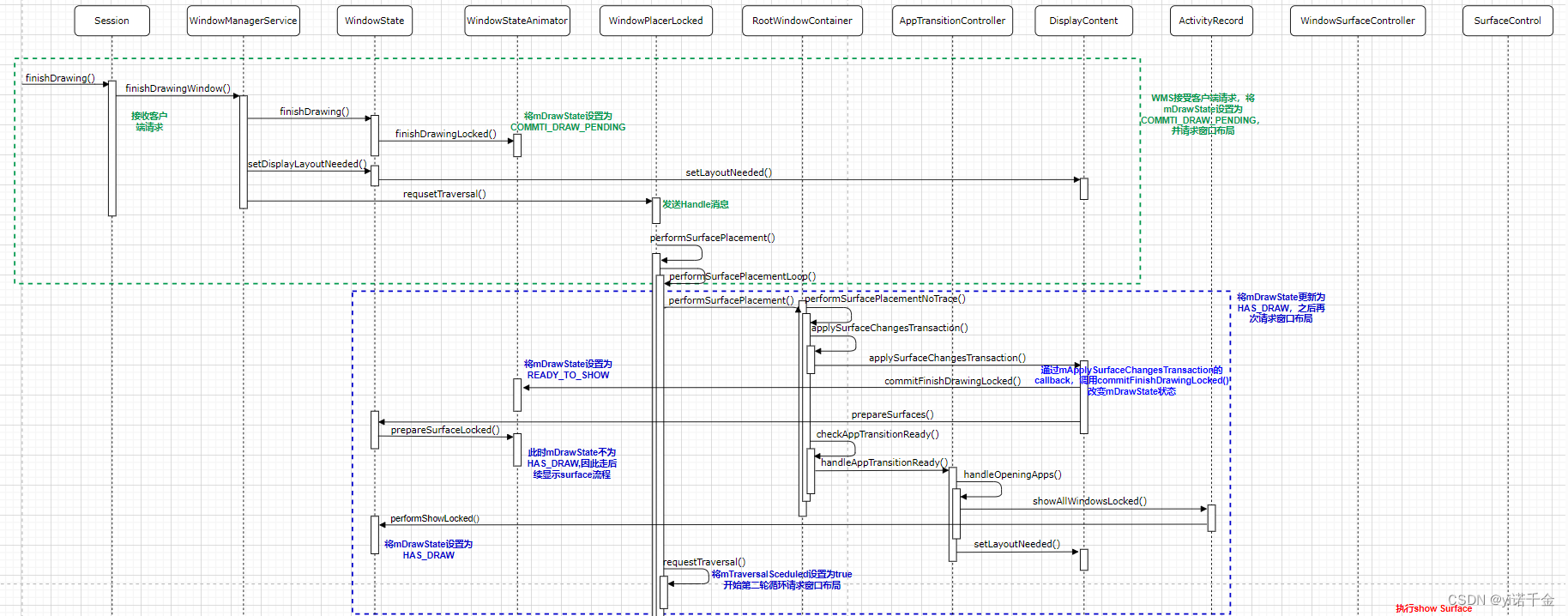
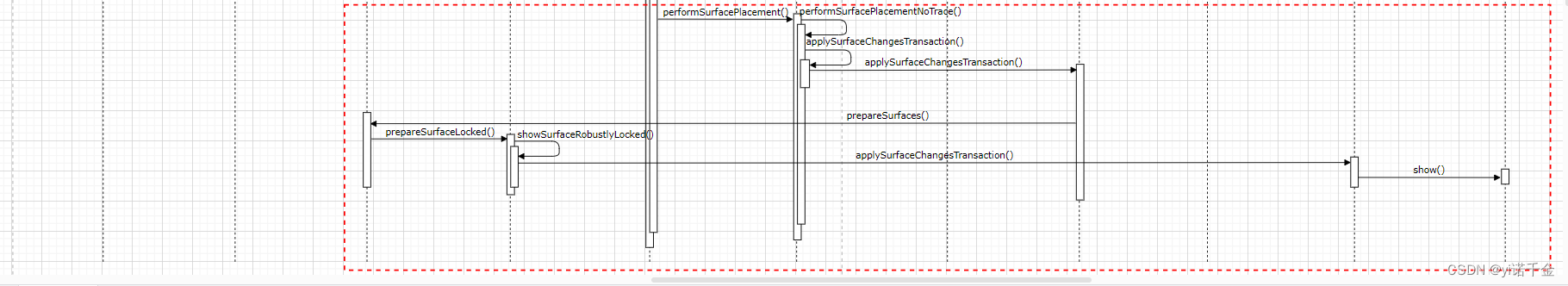
1.WMS接受客户端请求,将mDrawState更新为COMMIT_DRAW_PEDINGwin.finishDrawing(postDrawTransaction, seqId),并请求窗口布局mWindowPlacerLocked.requestTraversal();
2.通过mApplySurfaceChangesTransaction的callback,
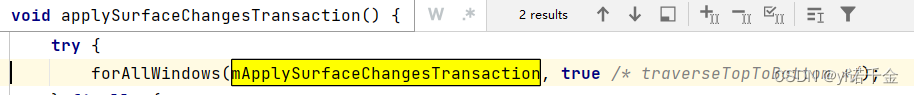
调用commitFinishDrawingLocked()

改变mDrawState状态将mDrawState更新为READY_TO_SHOW,
最终mDrawState更新为HAS_DRAW后,再次请求窗口布局
3.执行show Surface
showSurfaceRobustlyLocked(t)
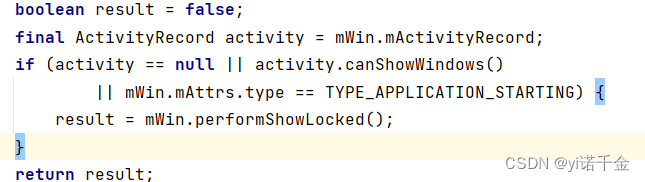
注:WindowStateAnimator的commitFinishDrawingLocked()方法中,如果是应用通过WindowManager中的addView的方式创建窗口,则不会有ActivityRecord,或者该窗口类型为启动窗口,则直接调用result = mWin.performShowLocked();,即WindowState的performShowLocked()方法改变窗口状态为HAS_DRAW,否则会从RootWindowContainer的checkAppTransitionReady方法逐步调用到performShowLocked()
4.窗口状态变化总结
WMS为了管理窗口的显示进度,在WindowStateAnimator中定义了mDrawState来描述Surface所处的状态。主要有如下五种状态:
NO_SURFACE:WMS添加窗口,即调用addWindow之后,还没有创建Surface,mDrawState处于该状态。
DRAW_PENDING:app调用relayoutWindow创建Surface后,但是Surface还没有进行绘制,mDrawState处于该状态。
COMMIT_DRAW_PENDING:app完成Surface的绘制,调用finishDrawing,将mDrawState设置为该状态。
READY_TO_SHOW:在performSurfacePlacement过程中会将所有处于COMMIT_DRAW_PENDING状态的mDrawState变更为READY_TO_SHOW。
HAS_DRAW:若准备显示窗口,WMS执行performShowLocked,将mDrawState设置为该状态

窗口显示相关方法 工作内容解释 addWindow App向WMS请求添加窗口记录,会在WMS里新建WindowState(NO_SURFACE) relayoutWindow App向WMS申请surface用于绘制,执行后window拥有了surface(NO_SURFACE->DRAW_PENDING) finishDrawingWindow App在surface上完成绘制后,通知WMS(DRAW_PENDING->COMMIT_DRAW_PENDING) commitFinishDrawingLocked WMS遍历window,对于完成绘制的window(COMMIT_DRAW_PENDING->READY_TO_SHOW) performShowLocked 判断系统是否允许窗口显示isReadyForDisplay(READY_TO_SHOW->HAS_DRAWN) showSurfaceRobustlyLocked 对HAS_DRAWN状态的窗口,用SurfaceControl通知SurfaceFlinger显示出来 5.移除流程简述
窗口移除从App端发起,当Activity执行destroy(),即以handleDestroyActivity()为起点,执行wm.removeViewImmediate()开启;
通过WindowManagerGlobal–>ViewRootImpl–>Session–>WindowManagerService的removeWindow(),调用到WindowState的removeIfPossible()–>removeImmediately(),接着调用到WindowStateAnimator的destroySurfaceLocked()–>destroySurface(),逐步调用改变绘制状态为NO_SURFACE–>WindowSurfaceController的destroy()最终调用到SurfaceControl的remove()来通知SurfaceFlinger来移除layer;
三、代码流程详解
1.客户端
1.1 Activity走到onresume后
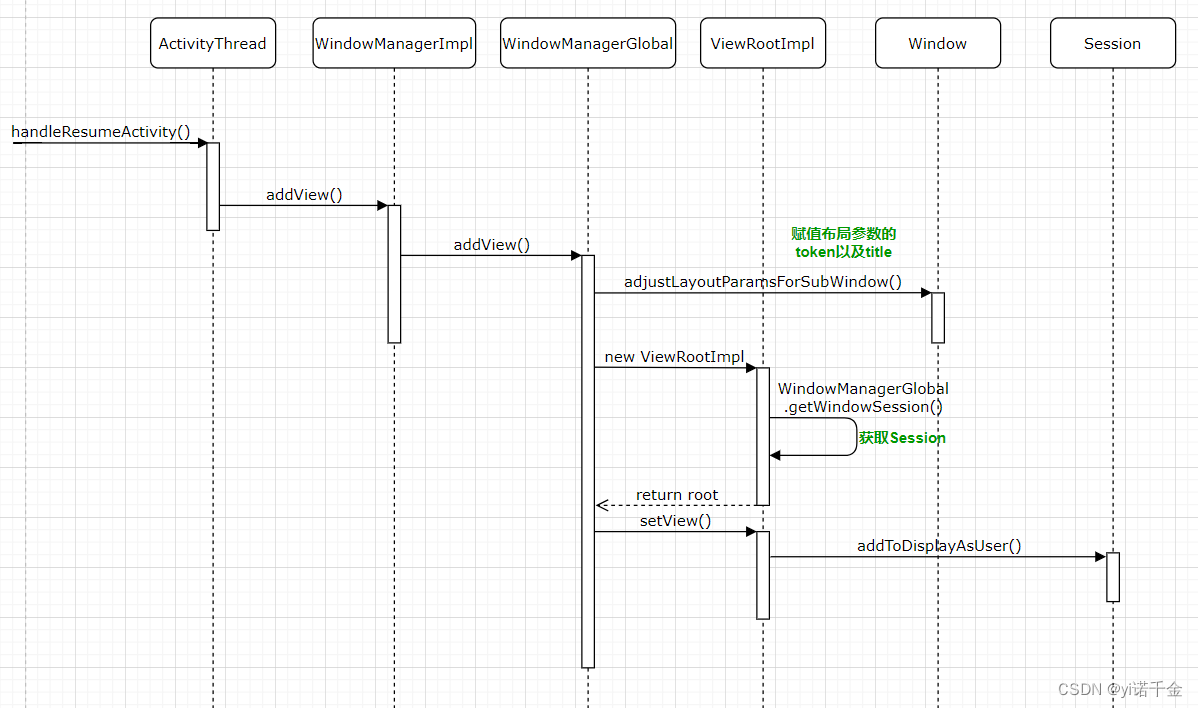
从ActivityThread.handleResumeActivity方法看起
1.调用performResumeActivity,执行onResume。
2.获取WindowManager的实现类WindowManagerImpl的实例。
3.调用WindowManagerImpl.addView传入DecorView和当前布局参数WindowManager.LayoutParams。
代码路径:framework/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java
@Override public void handleResumeActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, boolean finalStateRequest, boolean isForward, String reason) { ...... // TODO Push resumeArgs into the activity for consideration // skip below steps for double-resume and r.mFinish = true case. /*1.执行onResume*/ if (!performResumeActivity(r, finalStateRequest, reason)) { return; } ...... //获取Activity实例 final Activity a = r.activity; ...... // If the window hasn't yet been added to the window manager, // and this guy didn't finish itself or start another activity, // then go ahead and add the window. //mStartedActivity在performLaunchActivity和performResumeActivity方法中被置为false boolean willBeVisible = !a.mStartedActivity; ...... if (r.window == null && !a.mFinished && willBeVisible) { //获取当前Activity的PhoneWindow r.window = r.activity.getWindow(); //从PhoneWindow中获取DecorView View decor = r.window.getDecorView(); //将view的可见性状态设置为INVISIBLE,view不可见但是仍然占用布局空间 decor.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE); /*2.获取WindowManager的实现类WindowManagerImpl的实例*/ ViewManager wm = a.getWindowManager(); //获取布局参数 WindowManager.LayoutParams l = r.window.getAttributes(); //将phoneWindow的DecorView赋值给mDecor a.mDecor = decor; //设置窗口类型为TYPE_BASE_APPLICATION l.type = WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_BASE_APPLICATION; l.softInputMode |= forwardBit; if (r.mPreserveWindow) { a.mWindowAdded = true; r.mPreserveWindow = false; // Normally the ViewRoot sets up callbacks with the Activity // in addView->ViewRootImpl#setView. If we are instead reusing // the decor view we have to notify the view root that the // callbacks may have changed. ViewRootImpl impl = decor.getViewRootImpl(); if (impl != null) { impl.notifyChildRebuilt(); } } if (a.mVisibleFromClient) { if (!a.mWindowAdded) { a.mWindowAdded = true; /*3.传入DecorView和当前布局参数WindowManager.LayoutParams*/ wm.addView(decor, l); } else { // The activity will get a callback for this {@link LayoutParams} change // earlier. However, at that time the decor will not be set (this is set // in this method), so no action will be taken. This call ensures the // callback occurs with the decor set. a.onWindowAttributesChanged(l); } } } ...... }wm.addView(decor, l);WindowManager接口的实现是WindowManagerImpl,即实际调用的是WindowManagerImpl中的addView方法
代码路径:framework/core/java/android/view/WindowManagerImpl.java
@Override public void addView(@NonNull View view, @NonNull ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) { applyTokens(params); //转交给windowManagerGlobal,添加view mGlobal.addView(view, params, mContext.getDisplayNoVerify(), mParentWindow, mContext.getUserId()); }WindowManagerImpl对窗口的管理交给WindowManagerGlobal,调用WindowManagerGlobal的addView方法
WindowManagerGlobal中对窗口的处理主要如下几个步骤:
1.对WindowManagerImpl传进来的参数进行检查。
2.设置WindowManager.LayoutParams中的token、title等相关属性。查看“【1.2 Token的创建与传递】”。
3.创建ViewRootImpl对象,并获取客户端与WMS通信的Session。查看“【1.3 ViewRootImpl的创建】”。
4.在WindowManagerGlobal中备份DecorView,WindowManager.LayoutParams以及ViewRootImpl。
5.调用ViewRootImpl,与WMS通信添加窗口。查看“【1.4 ViewRootImpl与WMS的通信】”。
代码路径:framework/core/java/android/view/WindowManagerGlobal.java
public void addView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params, Display display, Window parentWindow, int userId) { /*1.对WindowManagerImpl传进来的参数进行检查*/ if (view == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("view must not be null"); } if (display == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("display must not be null"); } if (!(params instanceof WindowManager.LayoutParams)) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Params must be WindowManager.LayoutParams"); } final WindowManager.LayoutParams wparams = (WindowManager.LayoutParams) params; //此处的ParentWindow即当Activity的PhoneWindow if (parentWindow != null) { /*2.为wparams的token进行赋值*/ parentWindow.adjustLayoutParamsForSubWindow(wparams); } else { ...... } ViewRootImpl root; View panelParentView = null; synchronized (mLock) { ...... IWindowSession windowlessSession = null; ...... if (windowlessSession == null) { /*3.新建ViewRootImpl,在新建时会通过WindowManagerGlobal获取session*/ root = new ViewRootImpl(view.getContext(), display); } else { root = new ViewRootImpl(view.getContext(), display, windowlessSession); } view.setLayoutParams(wparams); /*4.在WindowManagerGlobal中备份DecorView,WindowManager.LayoutParams以及ViewRootImpl。*/ //当前view加入到view列表中 mViews.add(view); //将新建的viewRootImpl加入到root列表中 mRoots.add(root); //将当前布局参数加入到布局参数列表中 mParams.add(wparams); // do this last because it fires off messages to start doing things try { /*5.调用ViewRootImpl,设置view,panelParentView为null,与WMS通信添加窗口*/ root.setView(view, wparams, panelParentView, userId); } catch (RuntimeException e) { // BadTokenException or InvalidDisplayException, clean up. if (index >= 0) { removeViewLocked(index, true); } throw e; } } }1.2 Token的创建与传递
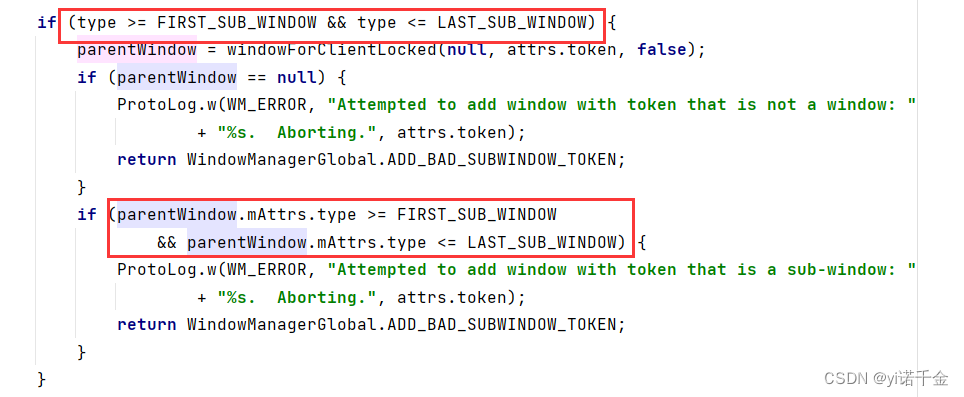
parentWindow.adjustLayoutParamsForSubWindow(wparams);调用Window的adjustLayoutParamsForSubWindow()方法
在adjustLayoutParamsForSubWindow中会分别对WindowManager.LayoutParams中的token以及title进行赋值。
1.首先针对子窗口、系统窗口以及应用窗口做了不同的处理,此处我们只关注应用窗口的处理。
2.其次将当前PhoneWindow.mAppToken赋值给WindowManager.LayoutParams.token。
代码路径:framework/core/java/android/view/Window.java
void adjustLayoutParamsForSubWindow(WindowManager.LayoutParams wp) { CharSequence curTitle = wp.getTitle(); if (wp.type >= WindowManager.LayoutParams.FIRST_SUB_WINDOW && wp.type //对子窗口的Token以及Title赋值 ...... } else if (wp.type = WindowManager.LayoutParams.FIRST_SYSTEM_WINDOW && wp.type //对子窗口的Token以及Title赋值 ...... } else { //对应用窗口的Token以及Title赋值 if (wp.token == null) { //将当前PhoneWindow的mAppToken赋值给wp.Token wp.token = mContainer == null ? mAppToken : mContainer.mAppToken; } //将Title设置为mAppName if ((curTitle == null || curTitle.length() == 0) && mAppName != null) { wp.setTitle(mAppName); } } //设置为packageName if (wp.packageName == null) { wp.packageName = mContext.getPackageName(); } ...... } //新建Token super(_service.mWindowManager, new Token(), TYPE_APPLICATION, true, null /* displayContent */, false /* ownerCanManageAppTokens */); ...... } ...... final Task task = r.getTask(); final Task rootTask = task.getRootTask(); ...... try { ...... try { ...... // Create activity launch transaction. /*将ActivityRecord.token封装在clientTransaction中*/ final ClientTransaction clientTransaction = ClientTransaction.obtain( proc.getThread(), r.token); final boolean isTransitionForward = r.isTransitionForward(); final IBinder fragmentToken = r.getTaskFragment().getFragmentToken(); clientTransaction.addCallback(LaunchActivityItem.obtain(new Intent(r.intent), System.identityHashCode(r), r.info, // TODO: Have this take the merged configuration instead of separate global // and override configs. mergedConfiguration.getGlobalConfiguration(), mergedConfiguration.getOverrideConfiguration(), r.compat, r.getFilteredReferrer(r.launchedFromPackage), task.voiceInteractor, proc.getReportedProcState(), r.getSavedState(), r.getPersistentSavedState(), results, newIntents, r.takeOptions(), isTransitionForward, proc.createProfilerInfoIfNeeded(), r.assistToken, activityClientController, r.shareableActivityToken, r.getLaunchedFromBubble(), fragmentToken)); ...... // Schedule transaction. /*将clientTransaction传递给客户端*/ mService.getLifecycleManager().scheduleTransaction(clientTransaction); ...... } catch (RemoteException e) { ...... } } finally { ...... } ...... return true; } ClientTransaction instance = ObjectPool.obtain(ClientTransaction.class); if (instance == null) { //创建ClientTransaction instance = new ClientTransaction(); } instance.mClient = client; /*把ActivityRecord.token存到mActivityToken*/ //private IBinder mActivityToken; instance.mActivityToken = activityToken; return instance; } final List final ClientTransactionItem item = callbacks.get(i); ...... /*将Token传递到LaunchActivityItem中*/ item.execute(mTransactionHandler, token, mPendingActions); item.postExecute(mTransactionHandler, token, mPendingActions); ...... } } Trace.traceBegin(TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "activityStart"); //将客户端传过来的Token保存在ActivityClientRecord的token中 ActivityClientRecord r = new ActivityClientRecord(token, mIntent, mIdent, mInfo, mOverrideConfig, mCompatInfo, mReferrer, mVoiceInteractor, mState, mPersistentState, mPendingResults, mPendingNewIntents, mActivityOptions, mIsForward, mProfilerInfo, client, mAssistToken, mShareableActivityToken, mLaunchedFromBubble, mTaskFragmentToken); client.handleLaunchActivity(r, pendingActions, null /* customIntent */); Trace.traceEnd(TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER); } ...... try { Application app = r.packageInfo.makeApplicationInner(false, mInstrumentation); ...... synchronized (mResourcesManager) { /*将ActivityClientRecord以及其对应的Token保存在mActivities中*/ //mActivities的类型为ArrayMap ...... /*将Token赋值给Activity.mToken*/ activity.attach(appContext, this, getInstrumentation(), r.token, r.ident, app, r.intent, r.activityInfo, title, r.parent, r.embeddedID, r.lastNonConfigurationInstances, config, r.referrer, r.voiceInteractor, window, r.activityConfigCallback, r.assistToken, r.shareableActivityToken); ...... } catch (SuperNotCalledException e) { throw e; } catch (Exception e) { ...... } return activity; } attachBaseContext(context); mFragments.attachHost(null /*parent*/); /*新建PhoneWindow*/ mWindow = new PhoneWindow(this, window, activityConfigCallback); ...... /*将客户端传过来的Token赋值给mToken*/ mToken = token; ...... /*PhoneWindow.mAppToken设置为当前客户端传递过来的Token*/ mWindow.setWindowManager( (WindowManager)context.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE), mToken, mComponent.flattenToString(), (info.flags & ActivityInfo.FLAG_HARDWARE_ACCELERATED) != 0); ...... } //传递客户端的mToken给appToken setWindowManager(wm, appToken, appName, false); } /** * Set the window manager for use by this Window to, for example, * display panels. This is /*把appToken赋值给mAppToken*/ mAppToken = appToken; mAppName = appName; mHardwareAccelerated = hardwareAccelerated; if (wm == null) { wm = (WindowManager)mContext.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE); } mWindowManager = ((WindowManagerImpl)wm).createLocalWindowManager(this); } this(context, display, WindowManagerGlobal.getWindowSession(), false /* useSfChoreographer */); } public ViewRootImpl(@UiContext Context context, Display display, IWindowSession session) { this(context, display, session, false /* useSfChoreographer */); } public ViewRootImpl(@UiContext Context context, Display display, IWindowSession session, boolean useSfChoreographer) { mContext = context; mWindowSession = session; ...... } synchronized (WindowManagerGlobal.class) { if (sWindowSession == null) { try { // Emulate the legacy behavior. The global instance of InputMethodManager // was instantiated here. // TODO(b/116157766): Remove this hack after cleaning up @UnsupportedAppUsage InputMethodManager.ensureDefaultInstanceForDefaultDisplayIfNecessary(); /*1.获取Binder*/ IWindowManager windowManager = getWindowManagerService(); /*2.调用WMS的openSession*/ sWindowSession = windowManager.openSession( new IWindowSessionCallback.Stub() { @Override public void onAnimatorScaleChanged(float scale) { ValueAnimator.setDurationScale(scale); } }); } catch (RemoteException e) { throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer(); } } return sWindowSession; } } /*新建Session*/ return new Session(this, callback); } setView(view, attrs, panelParentView, UserHandle.myUserId()); } /** * We have one child */ public void setView(View view, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs, View panelParentView, int userId) { synchronized (this) { if (mView == null) { mView = view; ...... //将布局参数拷贝纸mWindowAttributes mWindowAttributes.copyFrom(attrs); //设置包名 if (mWindowAttributes.packageName == null) { mWindowAttributes.packageName = mBasePackageName; } mWindowAttributes.privateFlags |= WindowManager.LayoutParams.PRIVATE_FLAG_USE_BLAST; attrs = mWindowAttributes; ...... // Keep track of the actual window flags supplied by the client. //获取当前布局的flags mClientWindowLayoutFlags = attrs.flags; ...... int res; /* = WindowManagerImpl.ADD_OKAY; */ // Schedule the first layout -before- adding to the window // manager, to make sure we do the relayout before receiving // any other events from the system. /*请求布局,对应服务端layoutWindow流程*/ requestLayout(); InputChannel inputChannel = null; if ((mWindowAttributes.inputFeatures & WindowManager.LayoutParams.INPUT_FEATURE_NO_INPUT_CHANNEL) == 0) { inputChannel = new InputChannel(); } ...... try { ...... /*与服务端进行Binder通信,调用Session的addToDisplayAsUser方法*/ //执行addWindow的相关流程 res = mWindowSession.addToDisplayAsUser(mWindow, mWindowAttributes, getHostVisibility(), mDisplay.getDisplayId(), userId, mInsetsController.getRequestedVisibilities(), inputChannel, mTempInsets, mTempControls); ...... } catch (RemoteException e) { ...... } finally { if (restore) { attrs.restore(); } } ...... if (DEBUG_LAYOUT) Log.v(mTag, "Added window " + mWindow); if (res
- setView
- addView
- addView
- handleResumeActivity






还没有评论,来说两句吧...