温馨提示:这篇文章已超过467天没有更新,请注意相关的内容是否还可用!
本摘要介绍了关于Yolov8 Opencv C++系列的保姆教程。该教程涵盖了如何使用Yolov8训练自己的数据集,并利用OpenCV库实现红绿灯识别及红绿灯故障检测的功能。通过本教程,读者可以学习到如何使用C++语言进行深度学习模型的训练和实际应用,特别是在智能交通领域中的红绿灯识别与故障检测方面的应用。
目录
一、Yolov8简介
1、yolov8 源码地址:
2、官方文档:
3、预训练模型百度网盘地址:
二、模型训练
1、标定红绿灯数据:
2、训练环境:
3、数据转化:
4、构造训练数据:
5、训练样本:
三、验证模型:
1、图像测试:
2、视频测试:
四、导出ONNX
五、Opencv实现Yolov8 C++ 识别
1、开发环境:
2、main函数代码:
3、yolov8 头文件inference.h代码:
4、yolov8 cpp文件inference.cpp代码:
一、Yolov8简介
1、yolov8 源码地址:
工程链接:https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics
2、官方文档:
CLI - Ultralytics YOLOv8 Docs
3、预训练模型百度网盘地址:
训练时需要用到,下载的网址较慢:
如果模型下载不了,加QQ:187100248.
链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1YfMxRPGk8LF75a4cbgYxGg 提取码: rd7b
二、模型训练
1、标定红绿灯数据:
类别为23类,分别为:
| red_light | green_light | yellow_light | off_light | part_ry_light | part_rg_light |
| part_yg_light | ryg_light | countdown_off_light | countdown_on_light | shade_light | zero |
| one | two | three | four | five | six |
| seven | eight | nine | brokeNumber | brokenLight |
标注工具地址:AI标注工具Labelme和LabelImage Labelme和LabelImage集成工具_labelimage与labelme-CSDN博客
 标注后图像格式
标注后图像格式 2、训练环境:
1)、Ubuntu18.04;
2)、Cuda11.7 + CUDNN8.0.6;
3)、opencv4.5.5;
4)、PyTorch1.8.1-GPU;
5)、python3.9
3、数据转化:
1)、需要把上面标定的数据集中的.xml文件转换为.txt,转换代码为:
import os
import shutil
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
from xml.etree.ElementTree import Element, SubElement
from PIL import Image
import cv2
classes = ['red_light', 'green_light', 'yellow_light', 'off_light', 'part_ry_light', 'part_rg_light', 'part_yg_light', 'ryg_light',
'countdown_off_light', 'countdown_on_light','shade_light','zero','one','two','three','four','five','six','seven',
'eight','nine','brokeNumber','brokenLight']
class Xml_make(object):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
def __indent(self, elem, level=0):
i = "\n" + level * "\t"
if len(elem):
if not elem.text or not elem.text.strip():
elem.text = i + "\t"
if not elem.tail or not elem.tail.strip():
elem.tail = i
for elem in elem:
self.__indent(elem, level + 1)
if not elem.tail or not elem.tail.strip():
elem.tail = i
else:
if level and (not elem.tail or not elem.tail.strip()):
elem.tail = i
def _imageinfo(self, list_top):
annotation_root = ET.Element('annotation')
annotation_root.set('verified', 'no')
tree = ET.ElementTree(annotation_root)
'''
0:xml_savepath 1:folder,2:filename,3:path
4:checked,5:width,6:height,7:depth
'''
folder_element = ET.Element('folder')
folder_element.text = list_top[1]
annotation_root.append(folder_element)
filename_element = ET.Element('filename')
filename_element.text = list_top[2]
annotation_root.append(filename_element)
path_element = ET.Element('path')
path_element.text = list_top[3]
annotation_root.append(path_element)
# checked_element = ET.Element('checked')
# checked_element.text = list_top[4]
# annotation_root.append(checked_element)
source_element = ET.Element('source')
database_element = SubElement(source_element, 'database')
database_element.text = 'Unknown'
annotation_root.append(source_element)
size_element = ET.Element('size')
width_element = SubElement(size_element, 'width')
width_element.text = str(list_top[5])
height_element = SubElement(size_element, 'height')
height_element.text = str(list_top[6])
depth_element = SubElement(size_element, 'depth')
depth_element.text = str(list_top[7])
annotation_root.append(size_element)
segmented_person_element = ET.Element('segmented')
segmented_person_element.text = '0'
annotation_root.append(segmented_person_element)
return tree, annotation_root
def _bndbox(self, annotation_root, list_bndbox):
for i in range(0, len(list_bndbox), 9):
object_element = ET.Element('object')
name_element = SubElement(object_element, 'name')
name_element.text = list_bndbox[i]
# flag_element = SubElement(object_element, 'flag')
# flag_element.text = list_bndbox[i + 1]
pose_element = SubElement(object_element, 'pose')
pose_element.text = list_bndbox[i + 2]
truncated_element = SubElement(object_element, 'truncated')
truncated_element.text = list_bndbox[i + 3]
difficult_element = SubElement(object_element, 'difficult')
difficult_element.text = list_bndbox[i + 4]
bndbox_element = SubElement(object_element, 'bndbox')
xmin_element = SubElement(bndbox_element, 'xmin')
xmin_element.text = str(list_bndbox[i + 5])
ymin_element = SubElement(bndbox_element, 'ymin')
ymin_element.text = str(list_bndbox[i + 6])
xmax_element = SubElement(bndbox_element, 'xmax')
xmax_element.text = str(list_bndbox[i + 7])
ymax_element = SubElement(bndbox_element, 'ymax')
ymax_element.text = str(list_bndbox[i + 8])
annotation_root.append(object_element)
return annotation_root
def txt_to_xml(self, list_top, list_bndbox):
tree, annotation_root = self._imageinfo(list_top)
annotation_root = self._bndbox(annotation_root, list_bndbox)
self.__indent(annotation_root)
tree.write(list_top[0], encoding='utf-8', xml_declaration=True)
def txt_2_xml(source_path, xml_save_dir, jpg_save_dir,txt_dir):
COUNT = 0
for folder_path_tuple, folder_name_list, file_name_list in os.walk(source_path):
for file_name in file_name_list:
file_suffix = os.path.splitext(file_name)[-1]
if file_suffix != '.jpg':
continue
list_top = []
list_bndbox = []
path = os.path.join(folder_path_tuple, file_name)
xml_save_path = os.path.join(xml_save_dir, file_name.replace(file_suffix, '.xml'))
txt_path = os.path.join(txt_dir, file_name.replace(file_suffix, '.txt'))
filename = file_name#os.path.splitext(file_name)[0]
checked = 'NO'
#print(file_name)
im = Image.open(path)
im_w = im.size[0]
im_h = im.size[1]
shutil.copy(path, jpg_save_dir)
if im_w*im_h > 34434015:
print(file_name)
if im_w im_w - 1:
xmax = im_w - 1
if ymax > im_h - 1:
ymax = im_h - 1
if w > 5 and h > 5:
list_bndbox.extend([name, flag, pose, truncated, difficult,str(xmin), str(ymin), str(xmax), str(ymax)])
if xmin im_w - 1 or ymin im_h - 1:
print(xml_save_path)
Xml_make().txt_to_xml(list_top, list_bndbox)
COUNT += 1
#print(COUNT, xml_save_path)
if __name__ == "__main__":
out_xml_path = "/home/TL_TrainData/" # .xml输出文件存放地址
out_jpg_path = "/home/TL_TrainData/" # .jpg输出文件存放地址
txt_path = "/home/Data/TrafficLight/trainData" # yolov3标注.txt和图片文件夹
images_path = "/home/TrafficLight/trainData" # image文件存放地址
txt_2_xml(images_path, out_xml_path, out_jpg_path, txt_path) 4、构造训练数据:
2)、训练样本数据构造,需要把分成images和labels,images下面放入图片,labels下面放入.txt文件:
 分成images和labels
分成images和labels  images
images  labels
labels 5、训练样本:
1)、首先安装训练包:
pip install ultralytics
2)、修改训练数据参数coco128_light.yaml文件,这个是自己修改的。
# Ultralytics YOLO 🚀, AGPL-3.0 license # COCO128 dataset https://www.kaggle.com/ultralytics/coco128 (first 128 images from COCO train2017) by Ultralytics # Example usage: yolo train data=coco128.yaml # parent # ├── ultralytics # └── datasets # └── coco128 ← downloads here (7 MB) # Train/val/test sets as 1) dir: path/to/imgs, 2) file: path/to/imgs.txt, or 3) list: [path/to/imgs1, path/to/imgs2, ..] path: /home/Data/TrafficLight/datasets # dataset root dir train: images # train images (relative to 'path') 128 images val: images # val images (relative to 'path') 128 images test: # test images (optional) # Parameters nc: 23 # number of classes # Classes names: 0: red_light 1: green_light 2: yellow_light 3: off_light 4: part_ry_light 5: part_rg_light 6: part_yg_light 7: ryg_light 8: countdown_off_light 9: countdown_on_light 10: shade_light 11: zero 12: one 13: two 14: three 15: four 16: five 17: six 18: seven 19: eight 20: nine 21: brokeNumber 22: brokenLight # Download script/URL (optional) #download: https://ultralytics.com/assets/coco128.zip
3)、执行 train_yolov8x_light.sh,内容为:
yolo detect train data=coco128_light.yaml model=./runs/last.pt epochs=100 imgsz=640 workers=16 batch=32
开始启动训练:
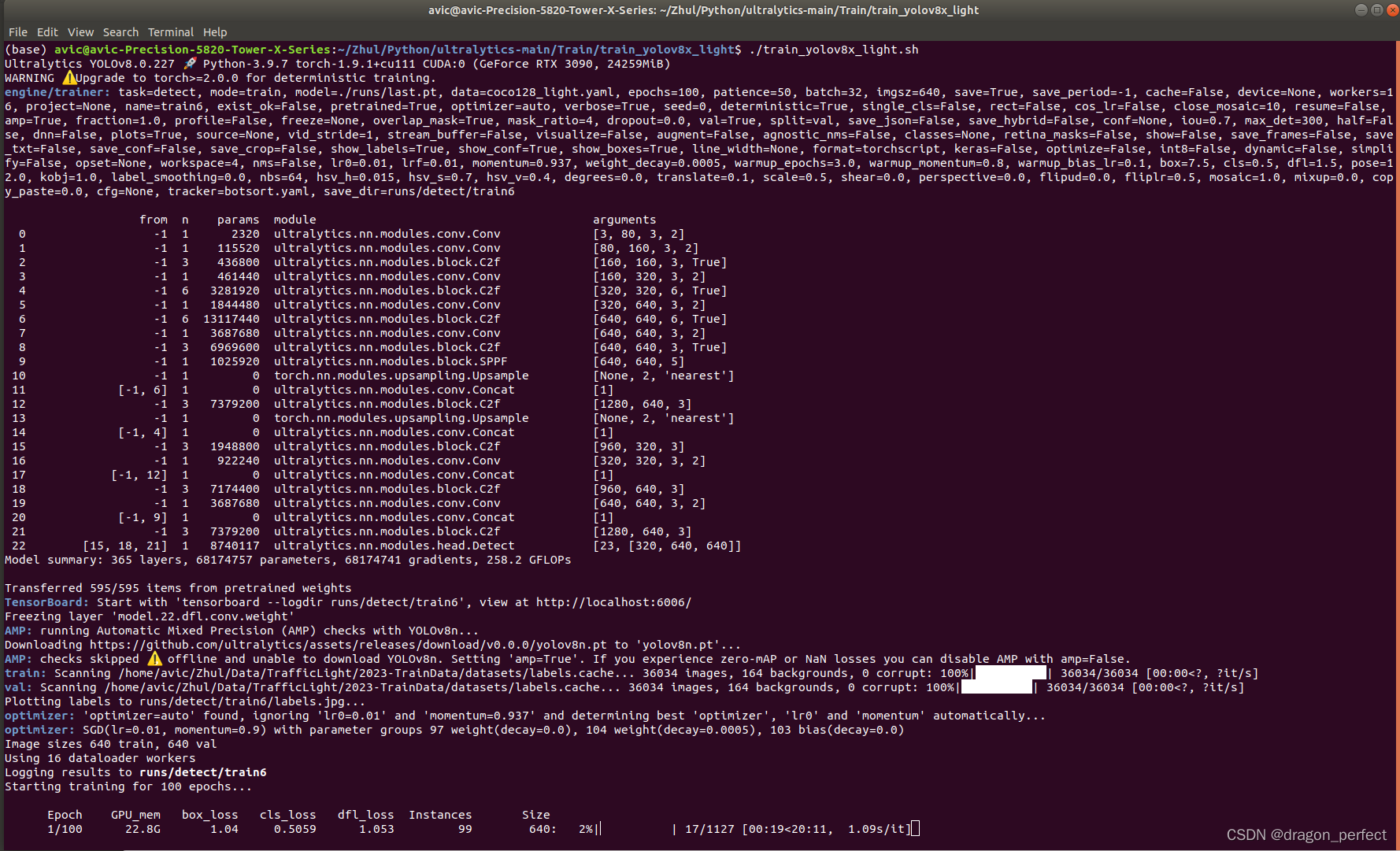 模型训练启动
模型训练启动 三、验证模型:
1、图像测试:
from ultralytics import YOLO
# Load a model
#model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt') # load an official model
model = YOLO('best.pt') # load a custom model
# Predict with the model
results = model('bus.jpg') # predict on an image
# View results
for r in results:
print(r.boxes) # print the Boxes object containing the detection bounding boxes 2、视频测试:
import cv2
from ultralytics import YOLO
# Load the YOLOv8 model
model = YOLO('best.pt')
# Open the video file
video_path = "test_car_person_1080P.mp4"
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(video_path)
# Loop through the video frames
while cap.isOpened():
# Read a frame from the video
success, frame = cap.read()
if success:
# Run YOLOv8 inference on the frame
results = model(frame)
# Visualize the results on the frame
annotated_frame = results[0].plot()
# Display the annotated frame
cv2.imshow("YOLOv8 Inference", annotated_frame)
cv2.waitKey(10) 四、导出ONNX
1、训练输出,经过上面的训练后,得到训练生成文件,weights下生成了best.pt和last.pt:
 训练数据生成文件
训练数据生成文件 2、等训练完毕后,利用best.pt生成best.onnx,执行命令如下:
yolo export model=best.pt imgsz=640 format=onnx opset=12
五、Opencv实现Yolov8 C++ 识别
1、开发环境:
1)、win7/win10;
2)、vs2019;
3)、opencv4.7.0;
2、main函数代码:
#include
#include
#include "opencv2/opencv.hpp"
#include "inference.h"
#include
#include
#define socklen_t int
#pragma comment (lib, "ws2_32.lib")
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
int getFiles(std::string path, std::vector& files, std::vector& names)
{
int i = 0;
intptr_t hFile = 0;
struct _finddata_t c_file;
std::string imageFile = path + "*.*";
if ((hFile = _findfirst(imageFile.c_str(), &c_file)) == -1L)
{
_findclose(hFile);
return -1;
}
else
{
while (true)
{
std::string strname(c_file.name);
if (std::string::npos != strname.find(".jpg") || std::string::npos != strname.find(".png") || std::string::npos != strname.find(".bmp"))
{
std::string fullName = path + c_file.name;
files.push_back(fullName);
std::string cutname = strname.substr(0, strname.rfind("."));
names.push_back(cutname);
}
if (_findnext(hFile, &c_file) != 0)
{
_findclose(hFile);
break;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
int main()
{
std::string projectBasePath = "./"; // Set your ultralytics base path
bool runOnGPU = true;
//
// Pass in either:
//
// "yolov8s.onnx" or "yolov5s.onnx"
//
// To run Inference with yolov8/yolov5 (ONNX)
//
// Note that in this example the classes are hard-coded and 'classes.txt' is a place holder.
Inference inf(projectBasePath + "/best.onnx", cv::Size(640, 640), "classes.txt", runOnGPU);
std::vector files;
std::vector names;
getFiles("./test/", files, names);
//std::vector imageNames;
//imageNames.push_back(projectBasePath + "/test/20221104_8336.jpg");
//imageNames.push_back(projectBasePath + "/test/20221104_8339.jpg");
for (int i = 0; i modelScoreThreshold)
{
confidences.push_back(confidence);
class_ids.push_back(class_id.x);
float x = data[0];
float y = data[1];
float w = data[2];
float h = data[3];
int left = int((x - 0.5 * w) * x_factor);
int top = int((y - 0.5 * h) * y_factor);
int width = int(w * x_factor);
int height = int(h * y_factor);
boxes.push_back(cv::Rect(left, top, width, height));
}
}
}
data += dimensions;
}
std::vector nms_result;
cv::dnn::NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, modelScoreThreshold, modelNMSThreshold, nms_result);
std::vector detections{};
for (unsigned long i = 0; i 





还没有评论,来说两句吧...